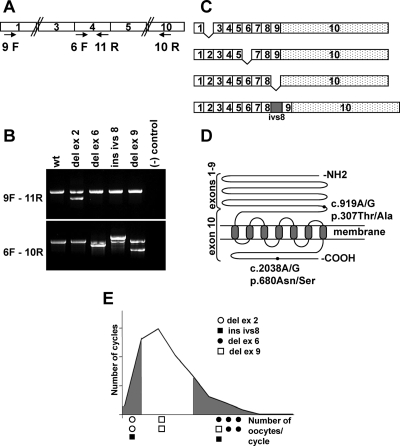
Figure 2.
RT-PCR analysis of FSHR. A, Schematic representation of RT-PCR primers used in nested PCR to amplify the FSHR cDNA. The numbered boxes indicate FSHR exons. B, RT-PCR products from patients carrying FSHR splicing variants. Upper and lower panels show amplification from exons 1–4 and 4–10, respectively. C, Schematic representation of the splicing variants detected in patients. D, Schematic representation of FSHR protein. The NH2 terminus constitutes the hormone binding domain, is extracellular, and is encoded by exons 1–9. The remaining protein is encoded by exon 10. The COOH terminus is intracellular. The positions of the two common polymorphisms are indicated by black circles. c, cDNA; p, protein. The nomenclature is according to the Human Genome Organization (HUGO) guidelines. E, Distribution of the splice variants along the graph of Fig. 1. del, Deletion; ins, insertion; ivs, intervening sequence (intron).