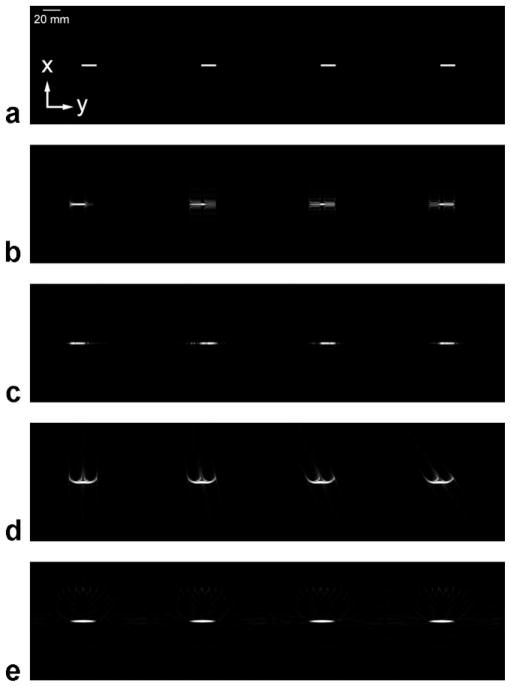
FIG. 4.
Computer simulations of the passage of a bolus of contrast through a blood vessel using different acquisition techniques. All images are MIPs of a 3D acquisition, and each image series consists of consecutive time frames (moving left to right) at the same points in time. The direction of blood flow is from left to right. The temporal resolution is 0.38 sec. (a) The truth image. (b) The spin-warp trajectory with elliptical centric ordering and the read-out direction parallel to the direction of blood flow. (c) The spin-warp trajectory with elliptical centric ordering and the read-out direction perpendicular to the direction of blood flow. (d) The 3D radial trajectory with linear ordering of views. (e) The 3D radial trajectory with pseudorandom ordering of views.