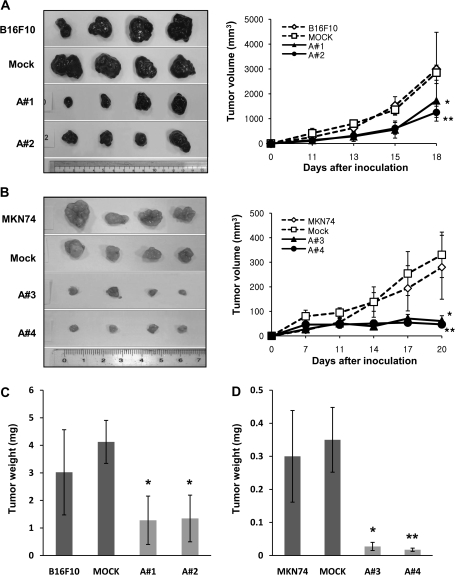
Figure 3.
Effect of mARD1A225 on primary tumor growth in mice. A) Representative images of primary tumor masses (left panel) and growth curves (right panel) are shown. C57BL/6 mice were injected subcutaneously with B16F10 (open diamond), B16F10-mock (open square), or B16F10-mARD1A225 cells (two clones; closed symbols). Results are means and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). *P = .003, **P < .001, compared with mock control cells, as determined with two-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). B) Representative images of primary tumor masses (left panel) and growth curves (right panel) are shown. Nude mice were injected subcutaneously with MKN74 (open diamond), MKN74-mock (open square), or MKN74-mARD1A225 cells (two clones; closed symbols). Results are means and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). *P = .007, **P < .001, compared with mock control cells, as determined with two-way repeated measures ANOVA. C) Tumor weights (n = 8 per group) were measured 3 weeks after inoculation with B16F10, B16F10-mock, or B16F10-mARD1A225 cells. Results are means and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). *P = .021, compared with mock control cells, as determined with the two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. D) Tumor weights (n = 10 per group) were measured 3 weeks after inoculation with MKN74, MKN74-mock, and MKN74-mARD1A225 cells. Results are means and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). *P = .017, **P = .015, compared with mock control cells, as determined with the two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. A#1= B16F10-mARD1A225 #1; A#2 = B16F10-mARD1A225 #2; A#3 = MKN74-mARD1A225 #3; A#4 = MKN74-mARD1A225 #4.