Figure 1.
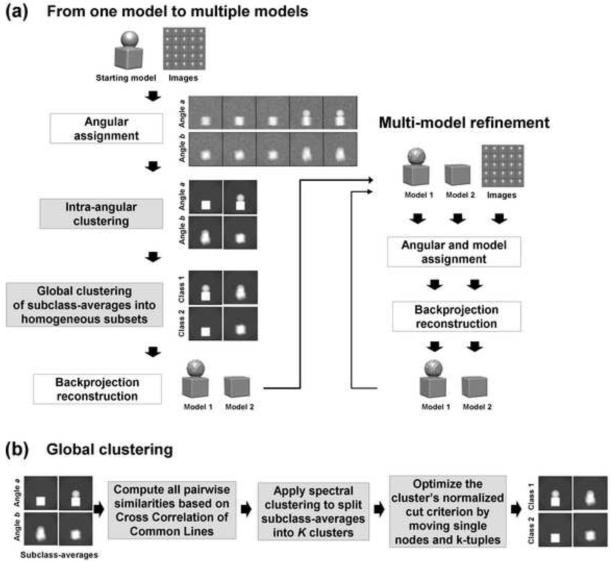
(a) Method flowchart. For illustrative purposes a two-model reconstruction process is shown, though the method is generally applicable for more than two models. Grey boxes refer to new approaches introduced in this work. The input is a starting model and a set of boxed images. On the left side, the images are clustered into two groups to generate the two initial models. In the “Angular assignment” step, Euler angles are assigned to the experimental images by aligning them against the model projections. In the “Intra-angular clustering” step, we apply clustering within each Euler angle based on Multivariate Statistical Analysis (MSA) to separate all images of a specific projection direction into two homogeneous groups. This results in two subclass-average images for each Euler angle. In the “Global clustering” step, subclass-averages are grouped into two global clusters where subclass-averages from the same Euler angle are assigned to different clusters. Two initial 3D models are reconstructed from the two global clusters of subclass-averages in the “Backprojection reconstruction” step. These two initial models are improved in the iterative two-model refinement procedure, the right part of the figure. In this process, first, all experimental images are reclassified to the most similar projections of the two models. Then, new models are computed and the two-model refinement procedure is repeated. (b) More detailed algorithmic presentation of the “Global clustering” stage from (a). First, similarities between all subclass-averages are computed. Next, subclass-averages are clustered into two groups by applying the Spectral Clustering method. In the last step, two clusters are iteratively optimized by improving the score based on the normalized cut criterion.