Figure 2.
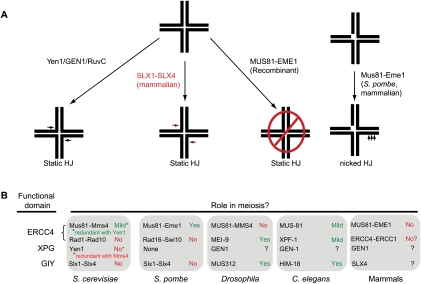
In vitro and in vivo activities of SSE that process HJs. (A) GEN1/Yen1 and the mammalian SLX1–SLX4 module contain classical HJ resolvase activities and can cleave static HJs symmetrically like the classical HJ resolvase RuvC. Recombinant MUS81–EME1 does not cleave static HJs, but has robust nHJ cleavage activity. (B) During meiosis, HJs are processed to produce crossover products. In budding yeast, Mus81–Mms4 and Yen1 have redundant roles in meiosis, while in fission yeast, Mus81–Eme1 is required for almost all meiotic events. In Drosophila, the SLX4 ortholog MUS312 and the ERCC4/XPF ortholog MEI-9 work in concert to affect meiotic crossovers. In worms, the situation is more complex, with HIM-18, MUS-81, and XPF-1 responsible for subsets of meiotic events. In mammals, it is still unclear what SSEs are required during meiosis, although there is no obvious meiotic phenotype in mice lacking MUS81.