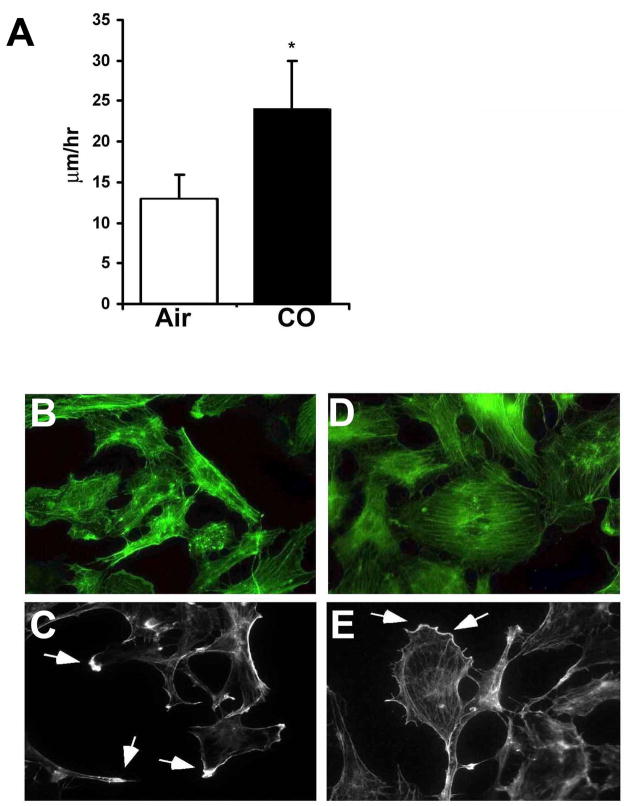
Figure 2. Carbon monoxide enhances motility and modulates cytoskeletal changes in RAEC.
A. Bar graph of the average speeds of RAEC along ± CO. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments. Results represent the mean distance traveled ± SD of 120 cells in each treatment group counted in three independent experiments. Five separate fields were monitored over the course of 24–48 hr with images taken of each field every 5 minutes. Values from 5 fields of CO and air treated cells were used to calculate mean± SD; One-way ANOVA; *p<0.02. Note that CO more then doubled the speed of cell migration following insult. B–E. Phalloidin staining of cells treated with air (A–B) or CO (D–E) for 24h. Arrows indicates the accumulation of F-actin at the leading edge of cells indicative of directed growth. Images are representative of 2 independent experiments from 6–10 images/slide in each treatment group.