Fig. 7.
Inducible expression of SpaA pilins.
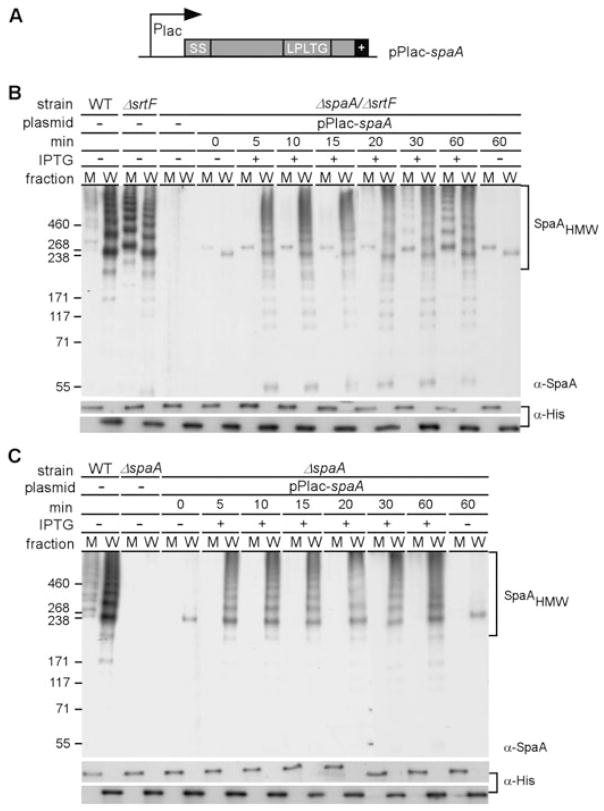
A. Plasmid pPlac-spaA was generated by cloning the coding sequence of spaA under the control of an IPTG-inducible promoter of the E. coli/C. diphtheriae shuttle vector pEKEx2.
B. Cells of the isogenic ΔsrtF or ΔsrtF-ΔspaA strain harbouring pPlac-spaA were induced by the addition of 1 mM IPTG, and samples with an equal number of cells were taken at timed intervals for isolating medium (M) and cell wall fragments (W) as described in Fig. 1. Samples of the wild-type and ΔsrtF bacteria were collected at the end of induction. Solubilized pilins were boiled in SDS sample buffer and were separated on 4–12% Tris-glycine gradient gels and detected by immunoblotting with the specific antiserum α-SpaA. Anti-his (α-His) and no IPTG (−) were used as controls.
C. The same treatment as described in (B) was employed for cells of the wild type (WT), its isogenic ΔspaA or ΔspaA strain harbouring pPlac-spaA.