Figure 1.
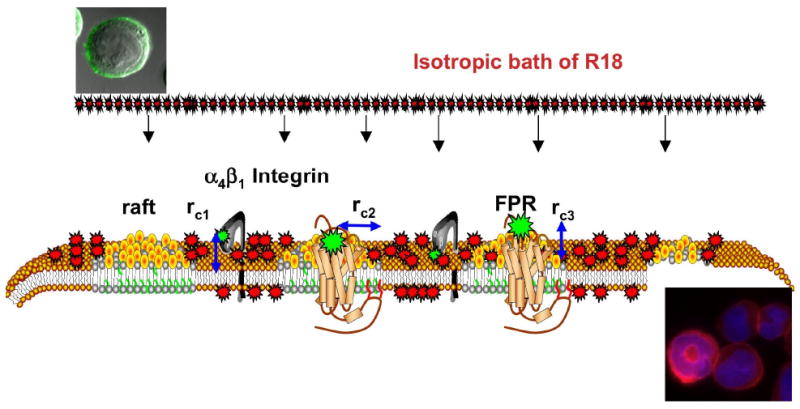
Model representation of exposure of cells to an isotropic environment of R18 results in spatio-temporally heterogeneous staining of the cell membranes in a manner that reflects heterogeneity of the plasma membrane. Sites of receptor expression are presented as fluorescently labeled ligands bound to α4β1 integrin localized in liquid disordered domains and formyl peptide receptor (FPR) localized in membrane rafts. Lipid components of membrane rafts such as cholesterol and sphingomyelin are believed to confer membrane-condensing properties that make them less permeable to exogenous probes.31-33 rci are the distances of closest approach between the FRET donor, FITC labeled ligands and R18 acceptors incorporated into the membrane. For the integrin rc1 = 25Å is equivalent to the vertical separation between the integrin headgroup that bears LDV-FITC and the membrane.17 For the FPR rci has vertical (height of the receptor binding site above the membrane, rc2 = 0) and lateral (width of the receptor and lipid raft that excludes R18 rc3 = 13Å) components. rci are based on X-ray crystal structure of the GPCR rhodopsin II (PDB # 1h68). Micrographs show a cell bearing LDV-FITC before and after mixing with R18.
