Figure 7.
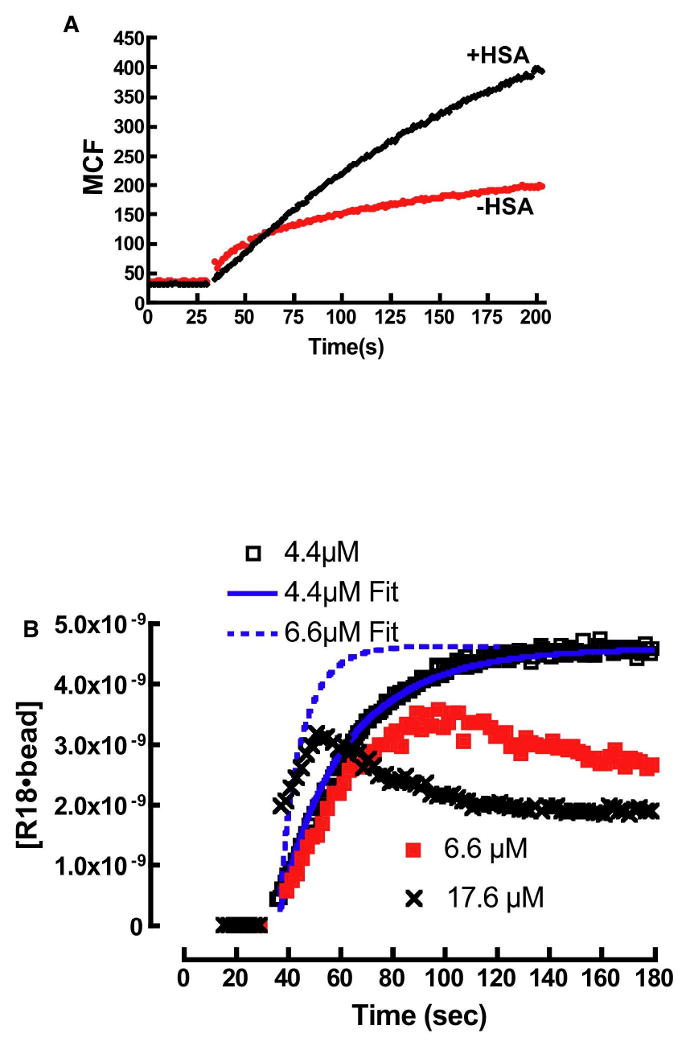
A. Plot of R18 binding to DOPC membranes in buffer containing 0.1% HSA and no HSA. In the absence of HSA the intensity of R18 is much lower than HSA containing media. B. Probe aggregation leads to anomalous binding kinetics of R18 to beads. At 4.4μM the equilibrium concentration of R18, [R18]eq is below the CAC and the binding curve shows agreement with a model (4.4μM Fit) that ignores the effects of aggregation (Eqn. 14). At 6.6μM the binding time-course for the binding of R18 to beads is shown to deviate from model predictions (6.6μM Fit). This is attributed to probe aggregation when the equilibrium concentration of free R18 exceeds CAC. The anomalous binding characteristics increase at 17.6μM.
