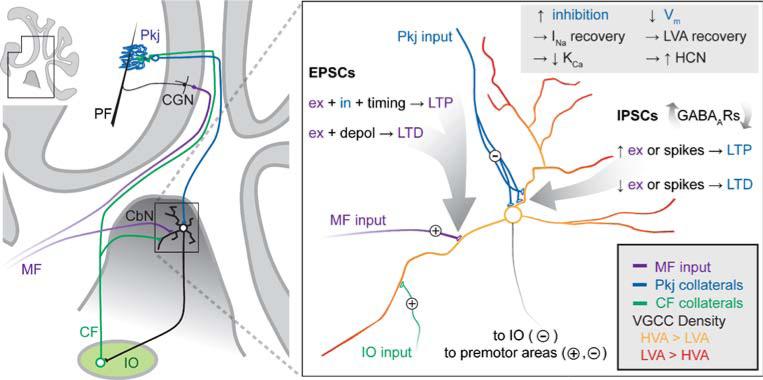
Fig. 1.
Schematic of sites of plasticity in the cerebellar nuclei. Left Schematic of a parasagittal section of the cerebellum (inset) with expanded region indicating that cerebellar nuclear neurons (CbN) project either to premotor areas (not shown) or to the inferior olive (IO). The IO forms the climbing fiber (CF) that targets Purkinje neurons (Pkj), with collaterals excite the CbN cells. Mossy fibers (MF) excite CbN cells as well as cerebellar granule neurons (CGN), which in turn form the parallel fibers (PF) that excite Pkj cells. Right Expansion of the cerebellar nuclear cell and its inputs, along with the sites and bases of plasticity. Note that small, usually inhibitory, cells project to the IO and large, usually excitatory cells project to premotor areas. Vm membrane voltage, INa voltage-gated Na current, LVA low-voltage activated (T-type) Ca current, KCa Ca-activated K current, HCN hyperpolarization-gated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, VGCC voltage-gated Ca channels, HVA high-voltage activated Ca channels, ex excitatory input, in inhibitory input, depol depolarization. Figure by J. S. Bant