Fig. 1.
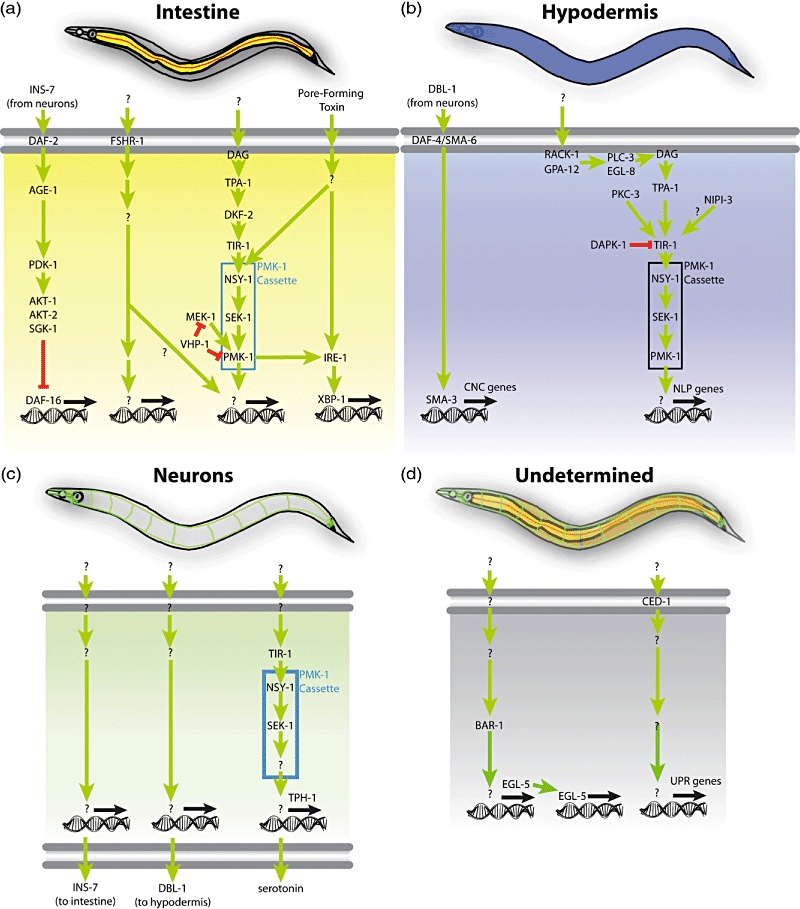
Diverse tissues participate in host defence in Caenorhabditis elegans. (a) The intestine (yellow) is a major immune organ. In it, insulin signalling regulates DAF-16/FOXO, a transcription factor involved in stress responses. A novel putative receptor, follicle stimulating hormone receptor (FSHR-1), acts in the intestine to presumably regulate signal transduction cascades that control the expression of pathogen-induced genes. A signalling pathway originating in diacylglycerol (DAG), produced presumably by phospholipase C, involves the protein kinase C homologue TPA-1 and the protein kinase D homologue DKF-2 to activate the PMK-1/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade that controls host defence genes. A parallel pathway, including MEK-1 and the protein phosphatase VHP-1, modulates PMK-1 activity. (b) In the hypodermis, an epidermal tissue in C. elegans, a non-canonical transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signalling pathway downstream of the heterodimeric TGF-β receptor formed by DAF-4 and SMA-6 regulates the SMAD homologue SMA-3 to control expression of caenacin genes (CNC) during infection with Drechmeria coniospora. In parallel, a pathway involving RACK-1 and GPA-12 (subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins), PLC-3 and EGL-8 (phospholipase C homologues), TPA-1 and PKC-3 (protein kinase C homologues), the Tribbles-like kinase NIPI-3 and the PMK-1 cassette regulates the expression of neuropeptide-like peptides (NLP) also during D. coniospora infection. In this pathway, the death-associated protein kinase (DAPK-1) regulates the PMK-1 cascade negatively at the level of or upstream of the protein scaffold TIR-1 (Toll, interleukin receptor). (c) In neurones, secretion of insulin INS-7 down-regulates DAF-16 in the intestine. Secretion of TGF-β DBl-1 regulates the SMA-3 in the hypodermis. Also, a poorly understood pathway including TIR-1, NSY-1 and SEK-1 regulates the production of serotonin via TPH-1; this PMK-1-independent pathway thus controls the aversive learning behaviour following infection. (d) It remains unknown where the BAR-1/β-catenin–EGL-5/HOX pathway controlling host response gene induction is required. Similarly, the locus of CED-1 activity for the induction of non-canonical unfolded protein response (UPR) genes remains to be determined.
