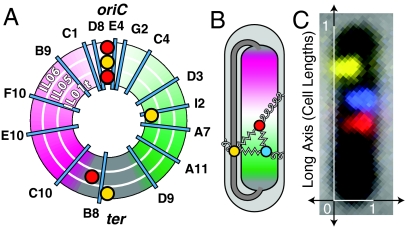
Fig. 1.
Experimental schematic: The E. coli fiducial strains (IL01t, IL05, IL06) each carry two fiducial fluorescent loci (red and yellow foci) in addition to a probe locus (cyan lines). (A) A schematic map of the genomic location of the probes by strain. The three concentric rings represent the three fiducial strains. (B) The left and right arms of the E. coli chromosome are positioned on opposite sides of the nucleoid, with the origin at midcell. The terminus-proximate loci are positioned at both ends of the nucleoid, as well as in a crossing region that bridges the two poles of the nucleoid. External positioning mechanisms, which position a locus directly relative to the cell, are represented by curly springs. Internal positioning mechanisms, which position loci relative to one another, are represented by zigzag springs. (C) A typical composite image for the “IL06 I2” strain.