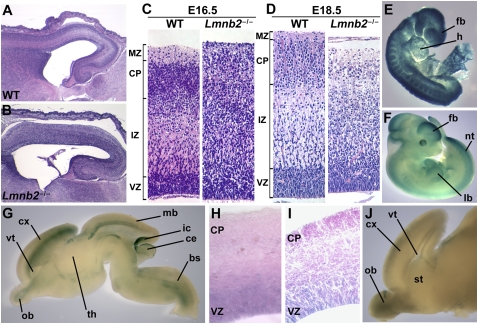
Fig. 2.
Abnormal patterning of the cerebral cortex in the setting of Lmnb2 deficiency. (A–D) Lmnb2 deficiency alters neuronal layering in the cerebral cortex. H&E staining of paraffin-embedded sections of cerebral cortex from E16.5 WT (A) and Lmnb2−/− (B) embryos. (C) Higher-magnification views of sections from the same E16.5 WT and Lmnb2−/− embryos. Cortical layers are indicated on the Left, from Top to Bottom: MZ, marginal zone; CP, cortical plate; IZ, intermediate zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Neuronal progenitors proliferate in the VZ; postmitotic cells leave the VZ and migrate along glial fibers to the CP. (D) Sections from E18.5 embryos showing similar defects. (E and F) Whole-mount β-galactosidase staining of Lmnb2+/− embryos at E8.5 (E) and E11.5 (F). Staining was ubiquitous at E8.5; at E11.5, staining was prominent in the forebrain (fb), midbrain, hindbrain, limb buds (lb), tailbud, somites, neural tube (nt), and retina. heart (h). (G) Whole-mount staining of an E16.5 Lmnb2+/− brain cut sagittally; β-galactosidase expression is found in the cortex (cx), olfactory bulb (ob), midbrain (mb), brainstem (bs), inferior colliculus (ic) and superficial layer of the cerebellum (ce); ventricle (vt); hypothalamus (th). (H) 40-μm section of the cortex of an E16.5 Lmnb2+/− embryo and (I) 20-μm section of the cortex of a newborn Lmnb2+/− pup, after β-galactosidase staining, revealing Lmnb2 expression in the VZ. (J) β-Galactosidase staining of the brain of a newborn Lmnb2+/− mouse, revealing Lmnb2 expression in the ob, cx, and vt.