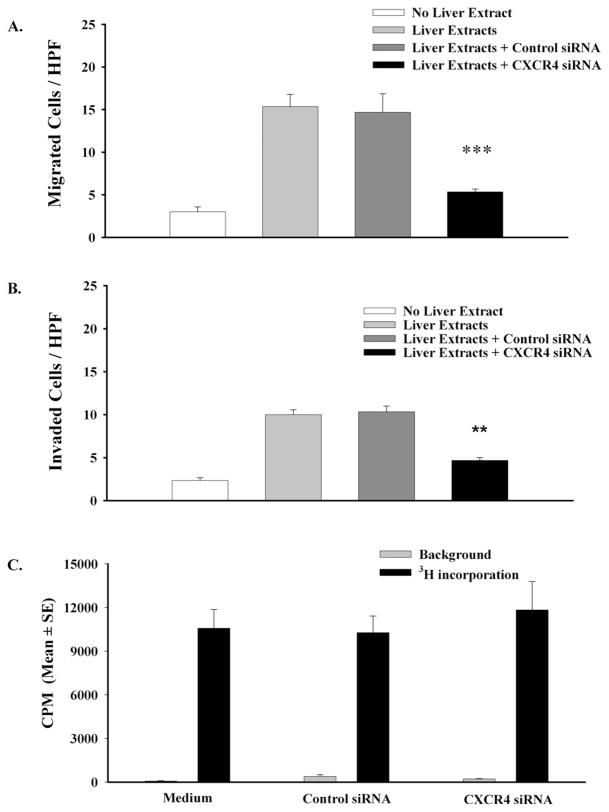
Figure 3.
CXCR4 siRNA inhibits chemotactic and chemoinvasive responses of human uveal melanoma cells but does not affect melanoma cell proliferation. Untreated and siRNA-transfected OCM3 uveal melanoma cells were placed in the top chambers of transwell culture plates. Protein extracts of either human liver or human smooth muscle (40 μg/mL) were added to the bottom chambers and served as chemoattractants to stimulate uveal melanoma cell migration to the bottom chambers. For chemotaxis assays, the top and bottom chambers were separated by a membrane with 8-μm pore size (A). For invasion assays, chambers were separated by a synthetic basement membrane created by coating an 8-μm pore membrane with basement membrane matrix (B). Twenty-four hours later, the number of melanoma cells that migrated to the bottom chamber was determined by counting the melanoma cells in 10 random HPFs using a compound microscope. This experiment was performed three times with similar results. Bars represent mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01. OCM3 melanoma cells were transfected with CXCR4 siRNA or control siRNA. Melanoma cell proliferation was assessed by uptake of [3H]thymidine after 48 hours in culture (C). P > 0.05 in all groups.