Figure 7. Inhibition of the PI3K pathway increases nuclear p27 in tumours.
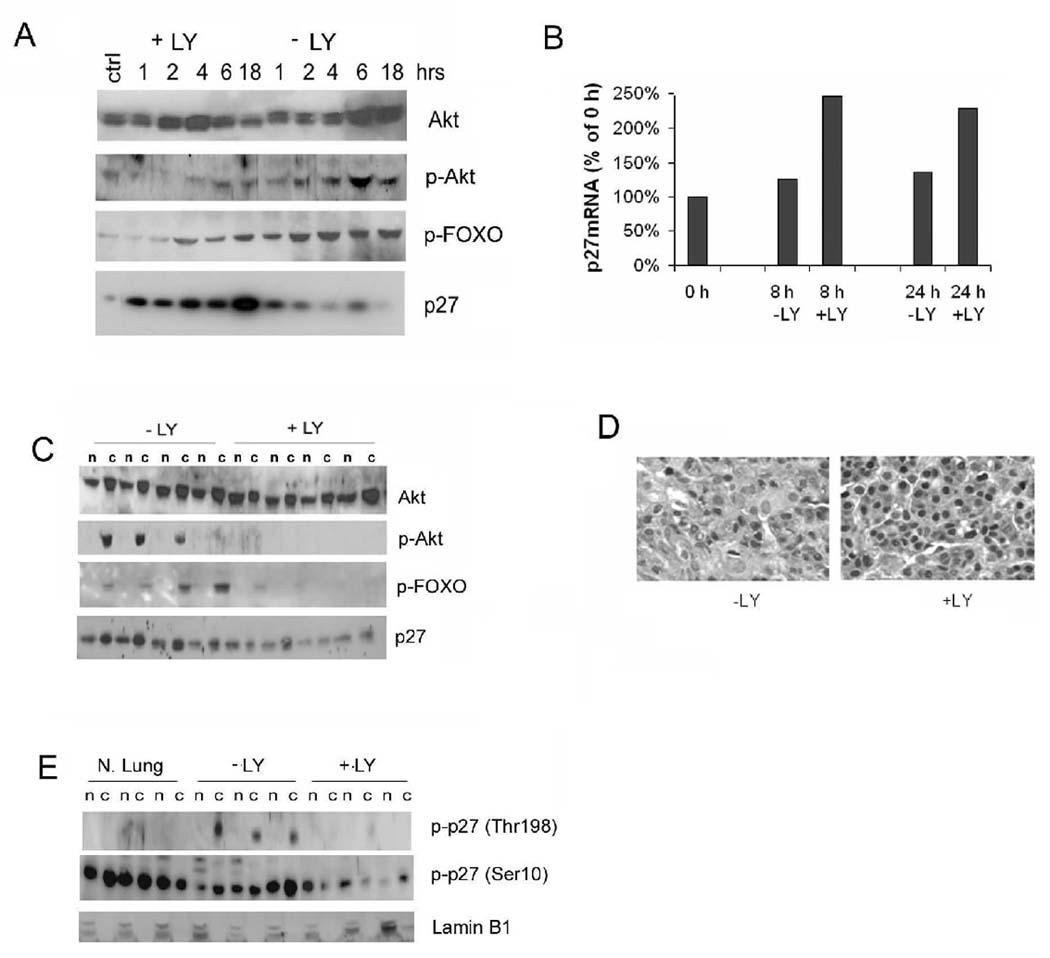
(A) Time course analysis of effects of LY294002 (LY) on SP10 mouse lung tumour cell line. Shown are Western blots of cell lysates probed with antibodies to p-Akt, p-FOXO, and p27 at the indicated times after addition of serum and LY. The control (ctrl) lane is from cells not serum starved. (B) Real-time PCR of p27 mRNA from treated (+LY) and control (−LY) treated SP10 cells 8 and 24 h after start of PI3K inhibition. (C) Western blot of total and p-Akt, p-FOXO, and p27 in lung tumours from wild type mice 5 h after treatment with LY. n: nuclear extracts, c: cytoplasmic fractions. (D) Sections of representative lung tumours immunostained for p27 shows increase in nuclear p27 following LY294002 treatment. (E) Western blot of tumour lysates shows decreased p-T198 p27 and p-S10 p27 in LY294002 treated lung tumours. Lamin B1 is nuclear fraction loading control. N.Lung = normal lung.
