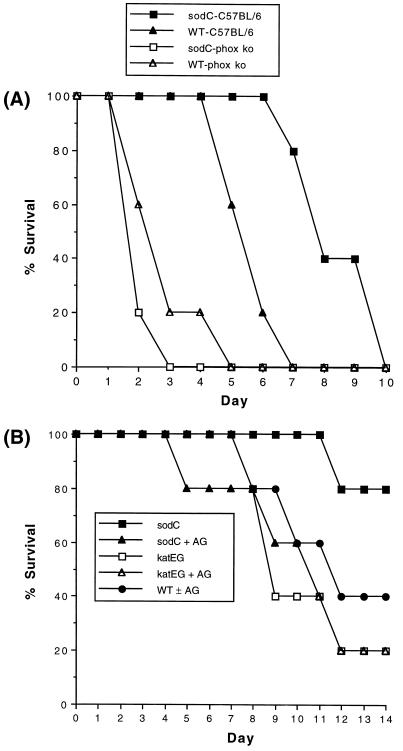
Figure 5.
(A) Virulence of sodC mutant S. typhimurium in wild-type and respiratory burst-deficient mice. C57BL/6 (Itys) and congenic phox-91 ko mice (19) were intraperitoneally challenged with wild-type or sodC mutant (MF1005) S. typhimurium. The time to death for wild-type and sodC mutant organisms was significantly different in C57BL/6 mice (P < 0.01) but not in phox ko (knock-out) mice (P > 0.05). (B) Virulence of sodC and katEG mutant S. typhimurium and the effect of NO synthase inhibition. C3H/HeN (Ityr) mice were intraperitoneally challenged with wild-type, sodC mutant (MF1005), or katEG mutant (XF1001) S. typhimurium. Separate groups of mice received drinking water treated with 2.5% (wt/vol) aminoguanidine (25) (AG), an inhibitor of inducible NO synthase. The survival of untreated mice challenged with sodC mutant organisms was significantly different from the other experimental groups (P < 0.01) after adjustment for multiple comparisons.