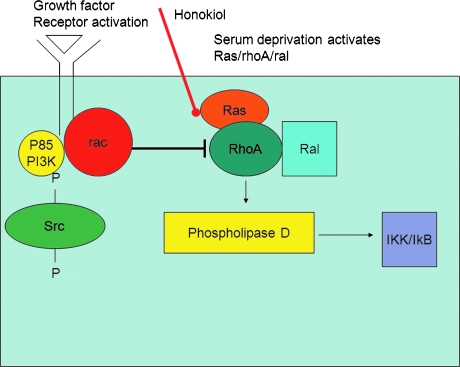
FIG. 2.
A possible chemical mechanism in which honokiol acts as a reactive oxygen (ROS) scavenger. This allows honokiol to act as a significant inhibitor in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-driven tumors. This inhibition is in part a result of the effect that honokiol has on the expression of phospholipase D (PLD) in the ras pathway. The direct effect of honokiol is on the Ras-RhoA-ral complex, which leads to the expression of phospholipase D (PLD). The expression of PLD from this complex is induced by rac, which is involved with PI3K and a receptor activated by growth factors. Ultimately, PLD activated IKK and IκB activity, which leads to tumor growth. The Ras-RhoA-ral is induced by serum deprivation. Studies have been done with the combination of both serum-deficient tumors with treatment of honokiol, varying from 10 to 15% deficient. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).