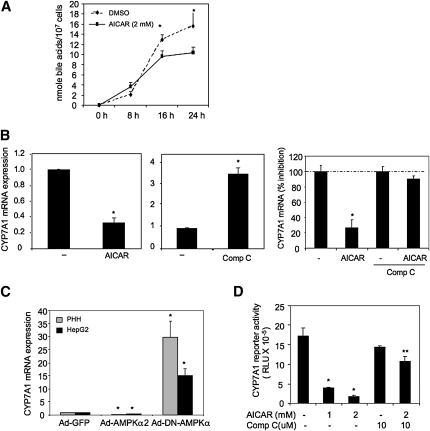
Fig. 3.
Activation of AMPK inhibits bile acid synthesis and CYP7A1 mRNA expression in hepatocytes. A: HepG2 cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO) or AICAR (2 mM) for the time and doses indicated. Total bile acids in culture media and cell lysates were quantified. B: Primary human hepatocytes (n = 3) were treated with vehicle (DMSO), 2 mM AICAR (left panel) or (10 μM) Compound C (middle panel), and HepG2 cells were pretreated with 10 μM compound C for 1 h followed by DMSO or AICAR (2 mM) (right panel) for 24 h. CYP7A1 mRNA expression levels were determined by real-time PCR. * indicates statistical significance, n = 3, P < 0.05, AICAR or Compound C-treated versus vehicle control (DMSO). C: Primary human hepatocytes (n = 3) or HepG2 cells were infected with Ad-GFP, Ad-AMPKα2, or Ad-DN-AMPK at MOI of 10 for 24 h. * indicates statistical significance, n = 3, P < 0.05, Ad-DNAMPKα2, or Ad-AMPKα2 versus Ad-GFP (control). D: Effect of AICAR and/or Compound C on human CYP7A1 reporter activity. HepG2 cells were transfected with a human CYP7A1 reporter (ph-1887-luc CYP7A1), and treated with AICAR and/or Compound C in the concentrations indicated. Reporter activities were assayed as described under Material and Methods. CYP7A1 mRNA expression was determined by real-time PCR. * indicates statistical significance, n = 3, P < 0.05, AICAR versus vehicle (DMSO) control; ** indicates statistical significance, n = 3, P < 0.05, Compound C + AICAR versus AICAR.