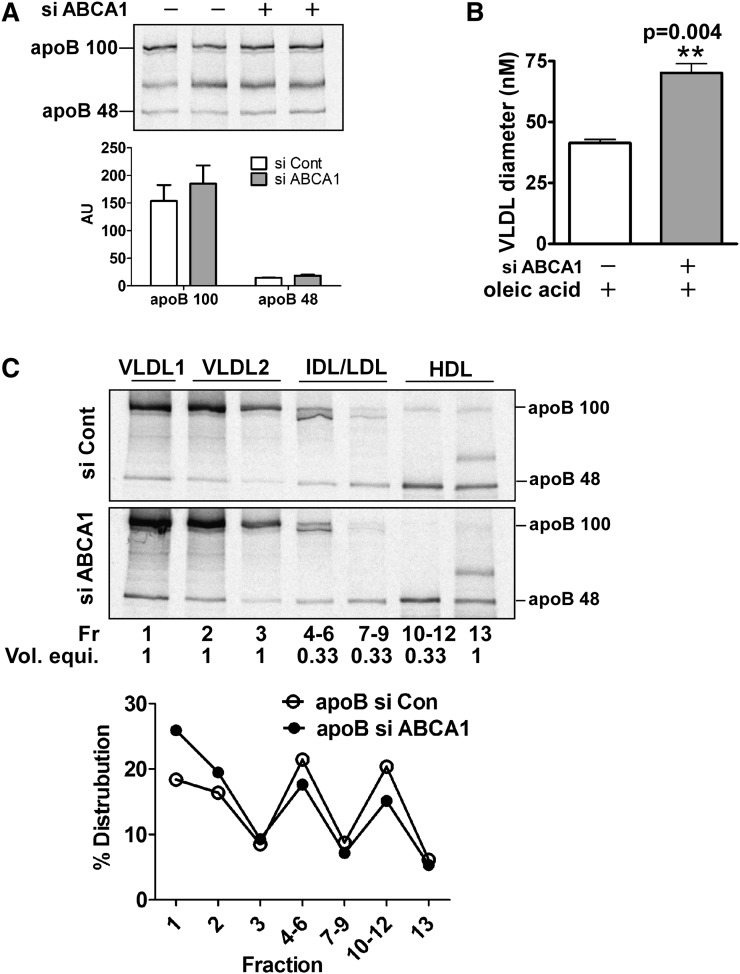
Fig. 2.
Silencing of ABCA1 promotes secretion of larger VLDL (i.e., VLDL1) with minimal increase in total apoB secretion. Control and ABCA1 siRNA-transfected McA cells were metabolically radiolabeled with [35S]Met (50μCi/ml) for 4 h in the presence of 0.8 mM oleate. A: Conditioned medium was immunoprecipitated with antibody to apoB. The immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by 4–8% SDS-PAGE and visualized with a phosphorimager. Relative intensities (mean ± range) of apoB100 and apoB48 were quantified and are shown under the image. AU, arbitrary units. B: VLDL from conditioned medium was floated by ultracentrifugation at d = 1.006g/ml and particle size was measured by dynamic laser light scatter. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of triplicate analyses. ** (P < 0.01). C: [35S]Met radiolabeled conditioned medium was subjected to density gradient ultracentifugation to fractionate the indicated lipoprotein species. ApoB was immunoprecipitated from one ml of individual or pooled fractions, the immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and radiolabel in protein bands was visualized using a phosphorimager. Because fractions 4–6, 7–9, and 10–12 were pooled (i.e., 3 ml total), the volume equivalent for each lane on the gel is indicated below the fraction number. Positions of lipoprotein classes in the gradient are denoted at the top of the gel and migration positions of apoB100 and apoB48 are shown on the right side of the gel image. VLDL1 = Sf 100–400, VLDL2 = Sf 20–100. Images were quantified using a phosphorimager and relative intensities of apoB (B100 + B48) in individual or pooled fractions are presented as a percentage distribution in the gradient. Intensities for the pooled fractions were multiplied by three to correct for the difference in total volume between individual (1 ml) and pooled fractions (3 ml).