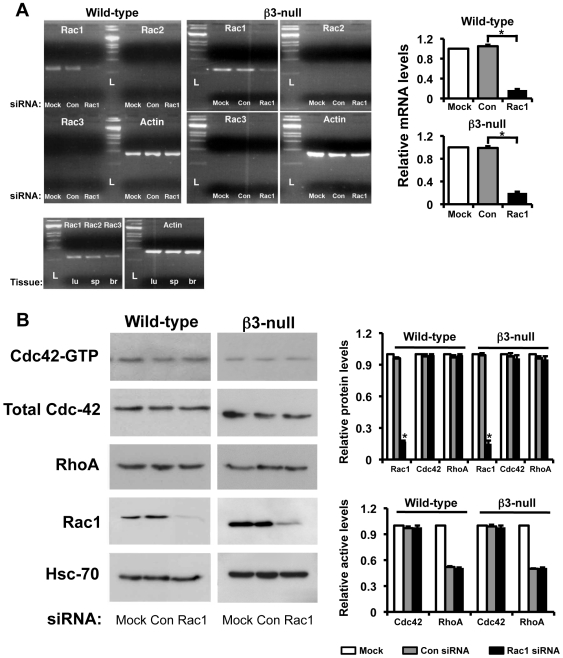
Figure 7. Rac1-depletion in endothelial cells does not affect the expression and activity of other Rho-related GTPases.
A. Analysis of mRNA expression of Rac isoforms by RT-PCR. RNA was extracted from wild-type and β3-null endothelial cells transfected with Con or Rac1 siRNA. As expected, mRNA expression of Rac1 was significantly reduced in Rac1-depleted cells of both genotypes (*P<0.001). Rac2 and Rac3 isoforms were not detected in either Con- or Rac1-siRNA transfected endothelial cells. Extracts of lung (lu), spleen (sp) and brain (br) act as positive controls for Rac1, Rac2 and Rac3, respectively. Actin mRNA provided the internal control. L: ladder. Bar graphs represent relative mRNA levels of Rac1 after Mock- (white), Con- (grey) and Rac1-siRNA (black) treatment in both genotypes. B. Western blot analyses show that Rac1 expression, as expected, was significantly reduced in Rac1-depleted cells of both genotypes (*P<0.01). In contrast, Cdc42 and RhoA protein expression was not significantly affected in endothelial cells after Rac1-siRNA in both genotypes. In addition, for both wild-type and β3-null endothelial cells active levels of Rac1, Cdc42 and RhoA were examined using GST-PAK pull-down (Rac1 and Cdc42) and G-LISA® (RhoA) assays on Mock (white), Con- (grey) and Rac1-siRNA (black) transfected cells. Bars graphs show mean relative protein (top) and active (bottom) levels (+ s.e.m.) of Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA in Mock (white), Con- (grey) and Rac1-siRNA (black) treated wild-type and β3-null cells. N = 3 independent experiments.