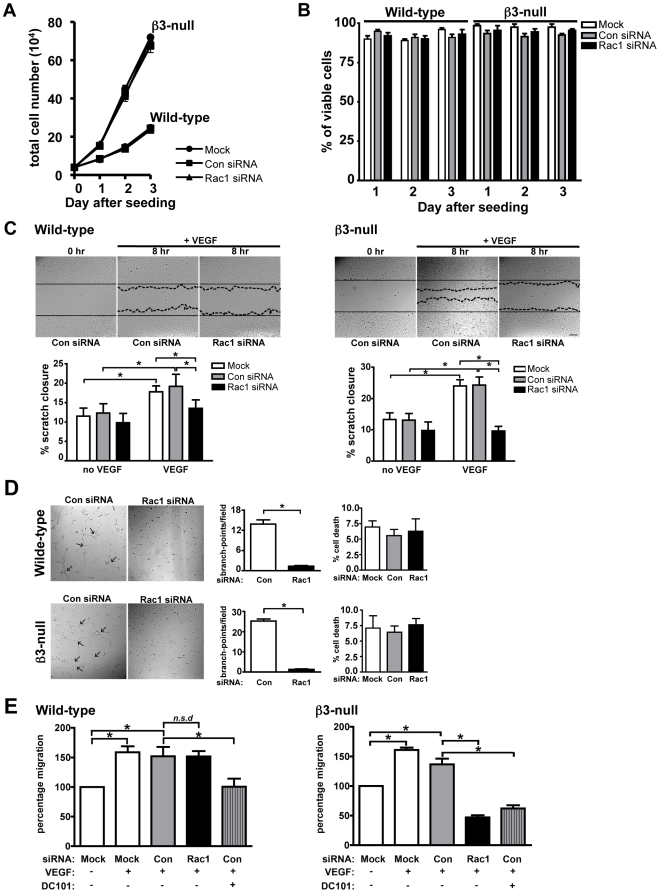
Figure 8. Effect of Rac1-depletion in wild-type and β3-null cells in 2D versus 3D.
A. Endothelial cell growth over 3 days was assessed by counting the total number of Mock, Con- or Rac1-siRNA transfected wild-type and β3-null endothelial cells. Although β3-null cells grew faster than wild-type, Rac1-depletion did not affect cell growth in either genotype. Symbols (•, Mock; ▪, Con-; and ▴, Rac1-siRNA) values given represent mean total cell numbers (+ s.e.m) from 3 independent experiments. B. Trypan blue exclusion, used to assess cell viability, shows that Rac1 knockdown has no effect on endothelial cell viability in either genotype. Bar graph represents mean percentage of viable cells (+ s.e.m) from 3 independent experiments. C. Wild-type and β3-null endothelial cell migration in response to VEGF was assessed in scratch wound healing assays. Representative photomicrographs (20 x magnification) of scratches at 0 hr and after 8 hr of migration after VEGF (25 ng/ml) stimulation. Bar graphs represent the mean percentage migration relative to 0 hours (+ s.e.m.), from 3 independent experiments, displayed by Mock (white), Con- (grey) and Rac1-siRNA (black) transfected wild-type and β3-null endothelial cells. Under 2D conditions, Rac1-depletion inhibited VEGF-induced migration of both wild-type and β3-null endothelial cell cells to baseline levels. D. VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell tube formation was assessed in 2D Matrigel cultures. Representative phase contrast micrographs (20 x magnification) showing cord structures (arrows) that formed 8 hr after seeding of Con- or Rac1-siRNA transfected cells on 2D Matrigel. Bar graphs represent mean numbers of branch points per field (+ s.e.m.) from 3 independent experiments. Rac1-depletion inhibited significantly VEGF-mediated tube formation by both wild-type and β3-null endothelial cells (*P<0.0001). Trypan blue exclusion assays demonstrated that the percentage of cell death of cells isolated from the cord-formation experiment did not change. Bar graph represents mean percentage of cell death (+ s.e.m.) from 3 independent experiments. E. In vitro VEGF-mediated endothelial cell migration was assessed in a modified 3D Boyden chamber assay. Quantification of VEGF-mediated migration of Mock, Con- or Rac1-siRNA transfected wild-type (left) and β3-null (right) endothelial cells in the presence or the absence of DC101. Bar graphs represent mean percentage migration relative to Mock treated cells in the absence of VEGF (+ s.d). VEGF-mediated migration was significantly reduced in Con siRNA DC101 treated endothelial cells, confirming the requirement of Flk-1 in VEGF-induced migration and provides a control (*P<0.05) siRNA targeting of Rac1 did not affect wild-type (n.s.d), but did inhibit β3-null, endothelial cell migration in 3D conditions (*P<0.01). N = 3–5 independent experiments.