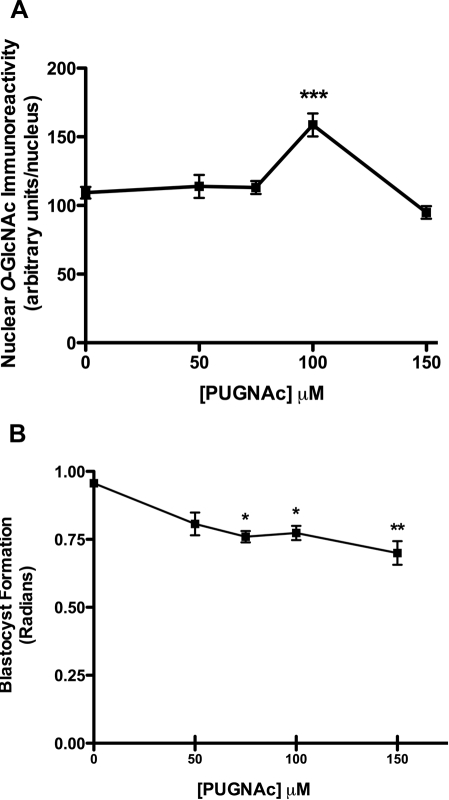
FIG. 3.
Effect of inhibition of O-GlcNAcase with PUGNAc on RL2 immunoreactivity (A) and blastocyst formation (B). Zygotes (18 h post-hCG) were cultured in KSOM (0.2 mM glucose), with increasing concentrations of PUGNAc to 96 h post-hCG, and blastocyst formation was assessed. A) A subset taken at 68 h post-hCG was immunolabeled with RL2 antiserum as described in Materials and Methods. Nuclear immunoreactivity was quantified using Image J software as described. For each treatment in each of three experiments, at least five embryos were analyzed, and data are presented graphically as mean nuclear O-GlcNAc immunoreactivity ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA revealed no interexperimental variation and a significant increase in RL2 immunoreactivity in response to 100 μM PUGNAc (***P < 0.01 by Tukey post hoc test, relative to control). B) Blastocyst formation was significantly decreased by increasing concentrations of PUGNAc. Each point represents the mean ± SEM from three separate experiments, each with a minimum of 10 embryos per treatment (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, relative to control by ANOVA and Tukey post hoc test).