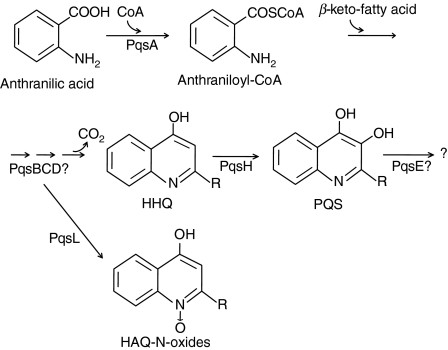
Figure 1.
Biosynthetic pathway of 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Anthranilate is activated by PqsA to form anthraniloyl-CoA, and this is condensed with β-keto-fatty acid to produce 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ). The condensation is postulated to be catalysed by PqsB, PqsC and PqsD. Alternatively, the intermediates in this pathway can be converted to HAQ-N-oxides by PqsL. HHQ is hydroxylated by PqsH to produce 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal).