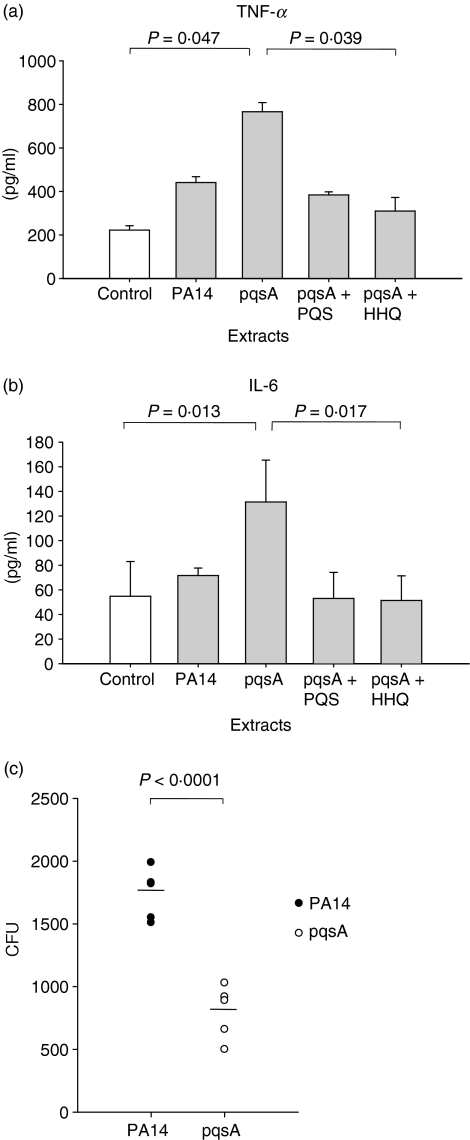
Figure 4.
Immune responses in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells (a,b) and pathogenicity in the lung (c). (a,b) The cells in the BAL fluid from C57BL/6 mice were harvested and cultured in vitro with extracts of culture supernatants from PA14 (wild-type) or a pqsA mutant in the presence or absence of 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ) or 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal) for 48 hr. The expression of tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the culture supernatants was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical differences among groups were analysed by a Kruskal–Walis test. (c) 1 × 105 colony-forming units (CFUs) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were injected into the lung of C57BL/6 mice intranasally (n = 5, each group). After 12 hr the mice were killed and lung lavage was performed. The lung was homogenized in 2 ml phosphate-buffered saline, and 100 μl of the lung homogenates were plated onto a Cetrimide agar (CA) plate to measure CFU. Statistical differences between groups were analysed by a Student’s t-test. All data (a–c) are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.