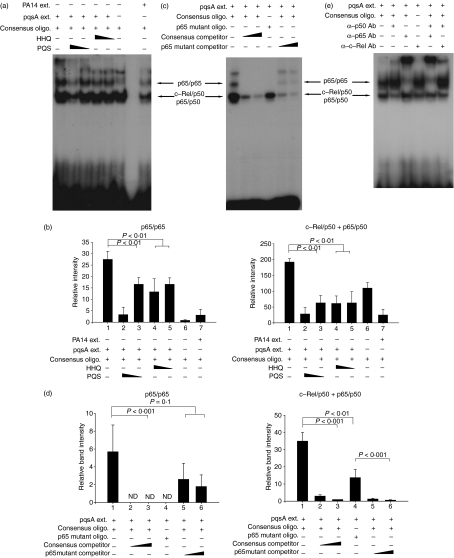
Figure 5.
4-Hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline (HHQ) and 2-heptyl-3,4-dihydroxyquinoline (PQS, Pseudomonas quinolone signal) suppress the binding of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) to its recognition site. J774A.1 cells were pre-treated with 1·12 or 0·28 μg/ml of HHQ or PQS for 2 hr, and treated with the extracts from pqsA (or PA14) culture supernatants for 30 min. After the cells were harvested, nuclear extracts were prepared and mixed with oligomers containing the NF-κB binding sites or its mutated sequences. The binding of NF-κB to the oligomers was measured by the electrophoretic mobility shift assay. All data (a,c,e) are representative of three or four independent experiments with similar results. (b) Densitometric analysis of Fig. 5(a). Band intensity of each band in scanned films was calculated by ImageJ program and combined before statistical analysis by analysis of variance (anova). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (d) Densitometric analysis of Fig. 5(c). Band intensity was calculated as for Fig. 5(b). Statistical analyses were performed by anova or Student’s t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 4).