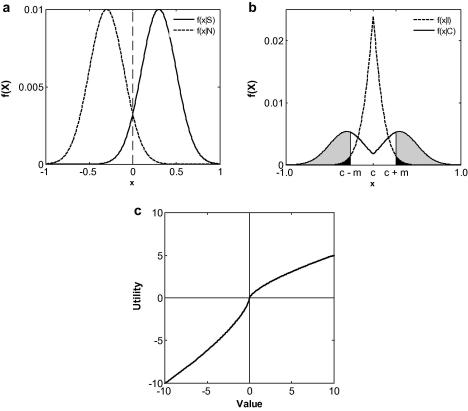
Fig. 1.
Computational model of post-decision wagering performance. (a) Theoretical distributions over a random variable X (corresponding to an arbitrary stimulus axis) for signal (S, solid line) and noise (N, broken line). (b) Probability distributions over different values of X for the probability of making a correct (solid line) and incorrect (broken line) categorisation. Shaded areas represent the integrals specified in Eqs. (9) (Hw, grey) and (10) (FAw, black). (c) Schematic of the loss-averse utility function used in the model.