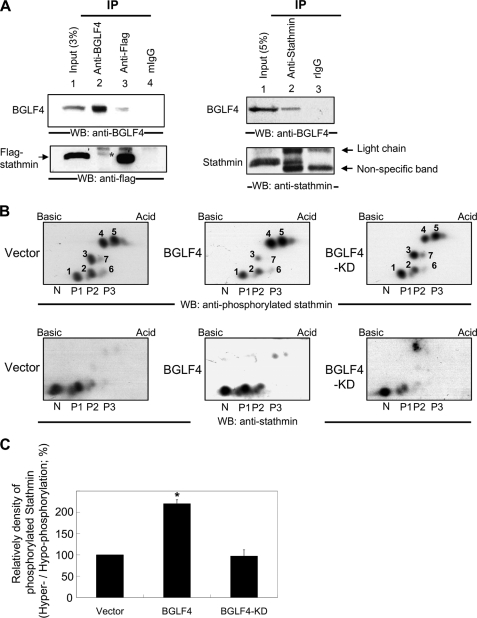
FIGURE 4.
BGLF4 interacts with stathmin and induces phosphorylation of stathmin in vivo. A, HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either pSG5-BGLF4 or pSG5-BGLF4 combined with pSG5-stathmin-Flag-expressing plasmids. Cell lysates were harvested 18 h post-transfection and immunoprecipitated by anti-BGLF4, anti-Flag antibodies, or mouse IgG antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblotting and then probed with anti-BGLF4, anti-Flag, or anti-stathmin antibodies. The Flag-tagged stathmin is indicated by the asterisk. B, inducible BGLF4, BGLF4-KD (BGLF4 kinase dead form), or vector control 293 T-REx cells were induced with 10 ng/ml doxycycline for 24 h. Lysates were subjected to two-dimensional PAGE and probed with anti-stathmin or anti-phosphorylated Ser-16 stathmin antibodies. N, nonphosphorylated form of stathmin. P1, stathmin isoforms which are phosphorylated at one phosphorylatable residue (dot 1); P2, stathmin isoforms which are phosphorylated at two phosphorylatable residues (dots 2 and 3); P3, stathmin isoforms which are phosphorylated at three phosphorylatable residues (dots 4 and 5). C, ratio for relatively density of hyperphosphorylated stathmin (dots 4 and 5) and hypophosphorylated stathmin isoforms (dots 1, 2, 3, 6, and 7) from the two experiments are plotted and statistically analyzed. *, significant difference to vector control (p < 0.05).