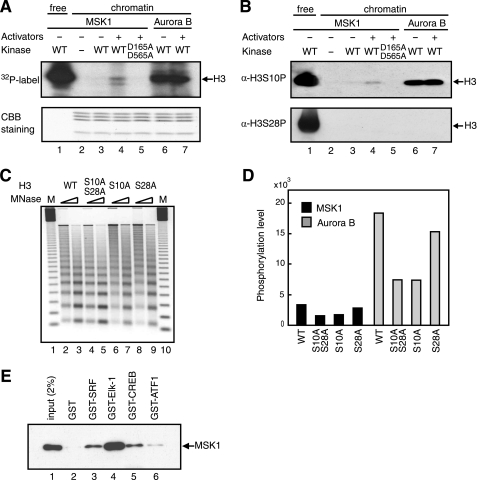
FIGURE 3.
MSK1 phosphorylates serine 10 of histone H3 within chromatin in an activator-dependent manner. A, 150 ng of the c-fos chromatin was incubated in the presence of 150 ng of MSK1 (lanes 3–5) or Aurora B (lanes 6 and 7) and 100 ng of the four activators (lanes 4, 5, and 7) using 10 mm [γ-32P]ATP. D195A/D595A is a kinase-deficient MSK1 (lane 5). 20 ng of free H3/H4 tetramer was phosphorylated by 400 ng of MSK1 as control (lane 1). The gel was stained in Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) (lower panel) and then exposed to an x-ray film (upper panel). WT, wild type. B, same sets of reactions as in A were performed in the absence of [γ-32P]ATP, and the phosphorylated residues were detected by immunoblotting using anti-H3-S10P (upper panel) or anti-H3-S28P (lower panel). C, chromatins assembled with wild-type (lanes 2 and 3) or mutant histone H3 whose serine was replaced with an alanine at both Ser-10 and Ser-28 (lanes 4 and 5), Ser-10 (lanes 6 and 7), or Ser-28 (lanes 8 and 9) were digested with two different concentrations of MNase. Molecular mass marker (M) is a 123-bp DNA ladder (lanes 1 and 10). D, kinase reactions were performed as in A, using the chromatin reconstituted with wild-type or mutant histones in the presence of MSK1 (black bars) or Aurora B (gray bars). The levels of phosphorylation were measured by ImageQuant software (GE Healthcare). E, GST (lane 2) or GST-fused activators (lanes 3–6) bound to glutathione-Sepharose 4B were incubated with FLAG-tagged MSK1, and the bound MSK1 was detected by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG M2 antibody. 2% of input FLAG-tagged MSK1 was loaded as control (lane 1).