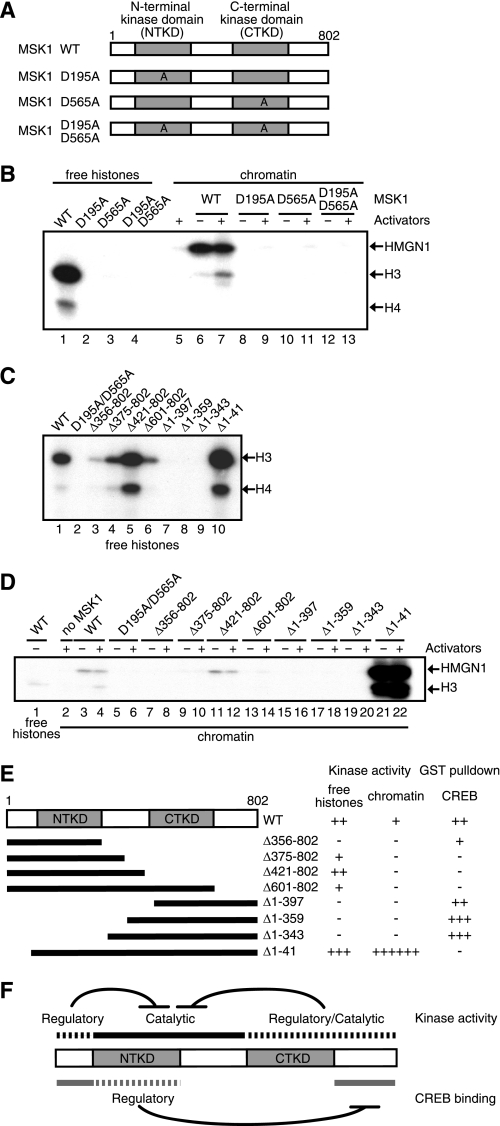
FIGURE 7.
Multiple domains within MSK1 are required for histone H3 phosphorylation. A, D195A, D565A, or D195A/D565A has an alanine in place of an aspartate at residue(s) 195, 565, or 195 and 565, respectively. WT, wild type. B, histone H3-H4 tetramers (lanes 1–4) or reconstituted chromatin (lanes 5–13) were phosphorylated by wild-type (lanes 1, 6, and 7) or mutant MSK1 (lanes 2–4 and 8–13). Mitogen- and stress-activated kinase (MSK) was omitted from lane 5. In the chromatin kinase assays, the reactions were performed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of activators (SRF, Elk-1, CREB, and ATF1). Phosphorylated HMGN1 and histones were detected by autoradiography. The positions of HMGN1 and histone H3 and H4 are indicated on the right. C, histone H3-H4 tetramers were phosphorylated by the deletion mutants of MSK1 as depicted in E. The positions of histone H3 and H4 are indicated on the right. D, chromatin kinase assays were performed with wild-type (lanes 3 and 4) or mutant MSK1 (lanes 5–22) in the presence or absence of activators. As controls, free histone H3-H4 tetramers were phosphorylated by wild-type MSK1 (lane 1). MSK1 was omitted from lane 2. E, schematic depiction of MSK1 deletion mutants and the summarized results of C and D as well as those of GST pulldown assays between the MSK1 mutants and CREB. No phosphorylation or interaction is indicated by −, and the approximate levels of phosphorylation or interaction are indicated by the increasing number of +. F, multiple intramolecular regulations control the kinase activity of MSK1 and its interactions with CREB.