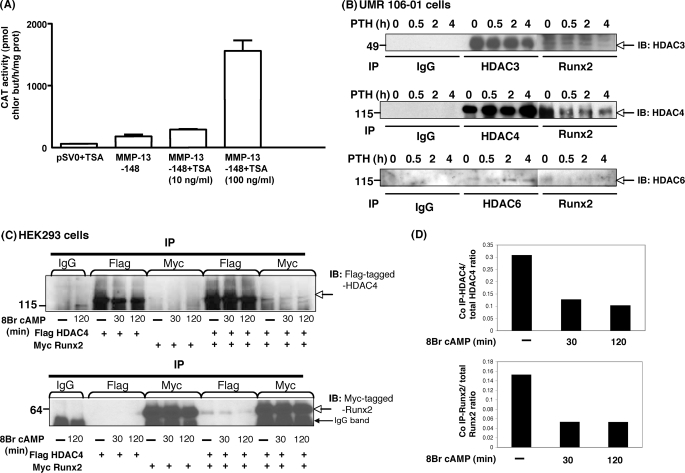
FIGURE 1.
HDACs inhibit MMP-13 and HDAC4 binds to Runx2 under basal conditions; after PTH stimulation, HDAC4 is released from Runx2. A, the −148 rat MMP-13 promoter construct was transiently transfected into UMR 106-01 cells, treated with control or trichostatin A (10 ng/ml or 100 ng/ml)-containing medium for 12 h, and then assayed for CAT activity. The data represent the means ± S.E. of three experiments. B, total cell lysates isolated from UMR 106-01 cells with or without PTH (10−8 m) treatment for 0 min, 30 min, 2 h, and 4 h were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Runx2 and HDAC3, HDAC4, or HDAC6 antibodies conjugated with protein A/G-agarose beads. The samples were examined by Western blot with anti-HDAC3, HDAC4, or HDAC6 antibody. C, HEK 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged HDAC4 or Myc-tagged Runx2 constructs. Total cellular lysates isolated from cells treated with 8-Bromo cAMP (10−3 m) for 30 or 120 min or control cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG and anti-Myc antibodies. The samples were examined by Western blot with anti-FLAG or anti-Myc antibodies. D, the expression level of HDAC4 or Runx2 was expressed as the ratio of co-immunoprecipitated FLAG HDAC4:total FLAG HDAC4 (top panel) or co-immunoprecipitated Myc Runx2:total Myc Runx2 (bottom panel).