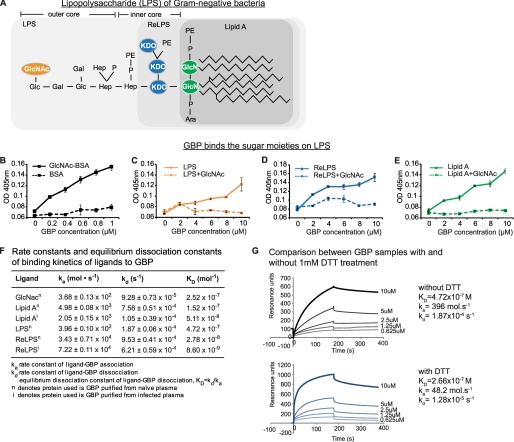
FIGURE 2.
GBP binds sugar moieties of LPS with high affinity. A, chemical structure of LPS. GlcNAc is located on the outer core of LPS. Hep, heptose; P, phosphate; PE, phosphoethanolamine; KDO, 3-deoxy-α-d-manno-octulosonic acid; Ara, arabinose. The outermost sugar residue of each LPS truncate is colored. B–E, ELISA to measure GBP-ligand binding. The GBP ligands (LPS, ReLPS, lipid A, LTA, or GlcNAc-bovine serum albumin (BSA)) were incubated overnight in binding buffer (see supplemental Materials and Methods) on 96-well PolysorpTM microplates. The unbound sites were blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin, and serially diluted GBP (with or without preincubation with GlcNAc) was added to each well. Anti-GBP antibody was added followed by horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary antibody. The peroxidase enzyme activity was determined at 405 nm. F, SPR-derived binding constants of GBP to LPS, LPS-truncates, or GlcNAc. The apparent KD values were calculated by using BIAevaluation software version 4.1. Suffix n and i refer to naïve (uninfected) and infected experimental conditions, respectively. G, SPR analysis of GBP binding with LPS, with and without dithiothreitol (DTT) treatment.