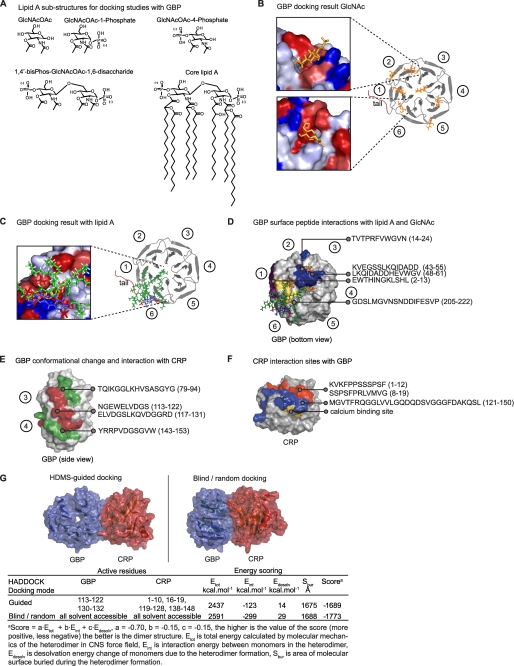
FIGURE 5.
Docking and identification of GBP surfaces that bind GlcNAc, lipid A, and/or CRP. A, GlcNAc and lipid A structures used for docking to GBP are shown. B, GlcNAc (orange) was docked to GBP, and binding energies were quantified. Circled numbers correspond to the Tectonin domains. Inset, GlcNAc were docked to the clefts (hydrophobic, red; hydrophilic, blue) between the propeller blades. C, lipid A (fatty acid chains, green; glucosamine, blue; phosphates, red) was docked to GBP. The lipid A molecule overlapped one of the GlcNAc binding sites. D–F, HDMS experiments are shown. D, GBP interaction sites with GlcNAc (blue)/lipid A (yellow). Peptides showing change in deuterium uptake were mapped onto the surface of GBP. GBPi showed an additional peptide (2–13) binding to lipid A (purple). Top docking results (GlcNAc, orange; lipid A, green-blue-red) are included for comparison. E, GBP interaction sites with CRP. Peptides involved in deuterium uptake (red, decrease; green, increase). F, CRP peptides that bind GBP. Surfaces in blue and red both showed decreased deuterium incorporation. The calcium (yellow) binding site on CRP is in close proximity and overlapping with the colored surfaces.