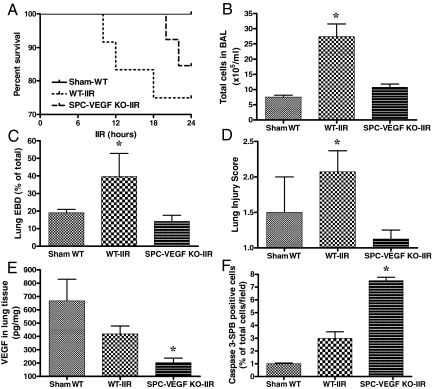
Figure 4.
Effects of VEGF knockout (KO) in type II cells on acute lung injury, VEGF intrapulmonary levels and alveolar epithelial apoptosis. A: Survival curves at 24 hours. B: BAL total cell count was significantly higher in WT-IIR group (n = 5) in comparison with Sham-WT (n = 3) and SPC-VEGF-KO-IIR mice (n = 6). *P < 0.01. C: The Evans blue dye assay for pulmonary vascular permeability was significantly higher in WT-IIR group (n = 8) in comparison with Sham-WT (n = 4) and SPC-VEGF-KO-IIR mice (n = 6). *P < 0.05. D: The lung injury score was significantly higher in the WT-IIR group (n = 7) in comparison with Sham-WT (n = 2) and SPC-VEGF KO-IIR mice (n = 4). *P < 0.05, WT-IIR versus SPC-VEGF-KO-IIR. E: VEGF concentration in lung homogenates, which was significantly lower in the SPC-VEGF-KO-IIR group (n = 9) in comparison with Sham-WT (n = 2) and WT-IIR mice (n = 7). *P < 0.05. F: Percentage of activated caspase-3/SP-B double positive cells in the alveolar walls, which was significantly higher in the SPC-VEGF KO-IIR group (n = 4), in comparison with Sham-WT (n = 3) and WT-IIR (n = 5) groups. *P < 0.001.