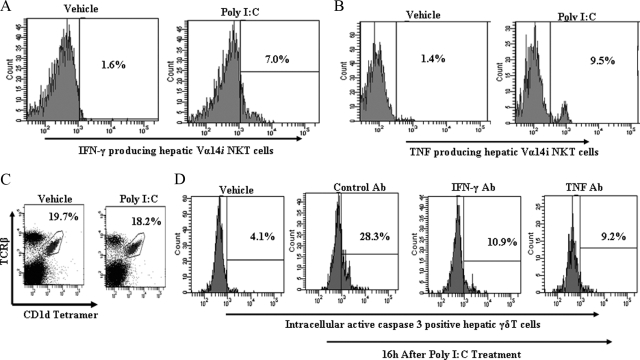
Figure 3.
Contribution of Vα14iNKT cell-derived cytokines to apoptosis of intrahepatic γδT cells after poly I:C treatment. A and B: C57BL/6 wild-type mice were treated with poly I:C or vehicle for 16 hours, and isolated hepatic Vα14iNKT cells were identified by FACS after cell surface staining with TCRβ mAb and PBS57-CD1d tetramer (described in Materials and Methods). The cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then stained intracellularly for IFN-γ or TNF. Representative FACS histograms demonstrating IFN-γ-positive hepatic Vα14iNKT cells and TNF-positive hepatic Vα14iNKT cells are shown in A and B, respectively, from two independent experiments of four mice per group. C: FACS dot plot (from two independent experiments of three mice per group) depicts hepatic Vα14iNKT cell profiles from poly I:C or vehicle-treated C57BL/6 wild-type mice at the 16-hour time point. D: C57BL/6 wild-type mice were pretreated with murine IFN-γ antiserum, murine TNF mAb, or control antibody before poly I:C treatment, and 16 hours later isolated hepatic γδT cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then stained intracellularly for active caspase 3. A representative FACS histogram highlighting active caspase 3-positive hepatic γδT cells from two independent experiments of four mice per group is shown.