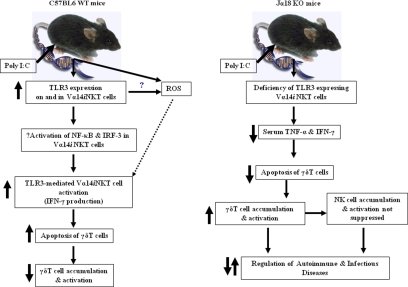
Figure 7.
A schematic model to illustrate the mechanisms of TLR3 ligand-dependent hepatic Vα14iNKT cell activation and the subsequent induction of apoptotic death of intrahepatic γδT cells on poly I:C application. Left panel: Vα14iNKT cells up-regulate TLR3 extracellularly on C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) mice on poly I:C treatment and activation of TLR3-expressing Vα14iNKT cells by poly I:C-induced Vα14iNKT cell cytokine production is through a signaling pathway, which could be dependent on the transcription factors nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF-3). Notably, these responses were suppressed by TLR3 deficiency. In addition, our study also revealed that the functional consequences of hepatic Vα14iNKT cell activation by the TLR3 ligand, poly I:C, is the negative regulation of γδT cells as shown by decreased accumulation of activated intrahepatic γδT cells due to apoptosis by Vα14iNKT cell-derived mediators (ie, cytokines and possibly ROS). Right panel: In contrast with that of C57BL/6 wild-type mice, poly I:C treatment of Jα18 KO mice was associated with lower serum levels of prototypical Vα14iNKT cell-derived cytokines (ie, TNF and IFN-γ), most likely due to a deficiency of TLR3-expressing activated hepatic Vα14iNKT cells. The functional consequence of lower cytokine levels is the suppression of apoptotic death of intrahepatic γδT cells (and thus increased survival of intrahepatic γδT cells) as shown by increased accumulation of γδT cells in the livers of poly I:C-treated Jα18 KO mice. Notably, the lack of suppression of hepatic NK cell accumulation and activation in Jα18 KO mice after poly I:C treatment may be due in part to the increased accumulation of γδT cells in the livers of these mice because we recently demonstrated that γδT cells promote NK cell accumulation in the liver after poly I:C treatment.43 Our study provides the first direct evidence that intrahepatic Vα14iNKT cells and γδT cells are functionally linked via TLR3 signaling on application of poly I:C because activated intrahepatic Vα14iNKT cells negatively regulate the recruitment, activation, and potentially harmful effector function(s) of intrahepatic γδT cells on application of the TLR3 ligand, poly I:C.