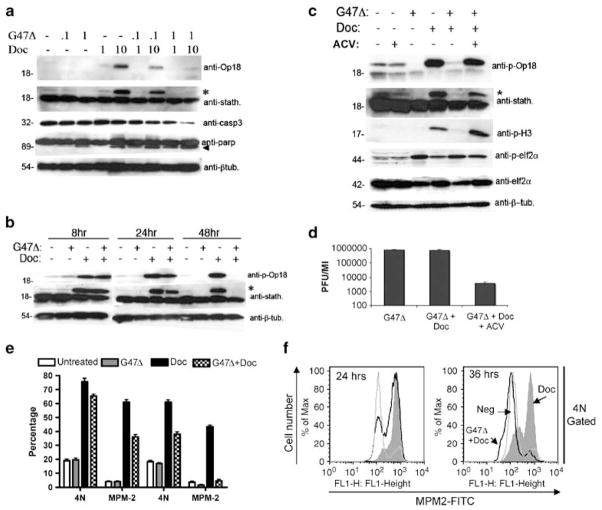
Figure 4.
Effects of G47Δ on Docetaxel-induced mitotically arrested cells. (a) Dose-dependent effects of G47Δ on docetaxel-induced op18/stathmin phosphorylation. LNCaP cells either remained untreated (−) or were inoculated with G47Δ (multiplicity of infection; MOI 0.1 or 1) in the presence or absence of docetaxel (1 or 10 nM) for 48 h. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with either anti-op18, which specifically detects op18 phosphorylated on serine-16 (23 kDa) or anti-stathmin, which recognizes both the unphosphorylated (18 kDa) and phosphorylated forms of op18. Asterisk (*) denotes the detection of the phosphorylated form of op18/stathmin using the anti-stathmin antibody. Combination of G47Δ and docetaxel also promotes enhanced cell death as detected by increased caspase-3 (casp3) and PARP cleavage. Arrowhead indicates the 89 kDa fragment of cleaved PARP. An anti-β-tubulin (β-tub.) was included as a loading control. Note that the decreased levels of full-length caspase-3 (32 kDa) reflects its activation. (b) Temporal-dependent effects of G47Δ (MOI 1) on docetaxel-induced op18/stathmin phosphorylation. Lysates were collected at 8, 24 and 48 h and immunoblotted with either anti-op18 anti-stathmin or anti-β-tubulin. (c) Acyclovir (ACV) attenuates the effects of G47Δ (MOI 1) on docetaxel-induced op18/stathmin phosphorylation. Similar results were obtained when lysates were probed with the mitotic-specific marker anti-phospho-histone-H3 (p-H3). Lysates were also probed with either anti-phospho-eIF2α or anti-eIF2α to show that the effects of G47Δ on docetaxel-induced mitotic block do not influence the phosphorylation status of eIF2α. (d) Single burst assays were performed in parallel to demonstrate the effectiveness of acyclovir on G47Δ replication 48 h after infection. (e) Cell-cycle analysis on the effects of G47Δ on mitotically arrested cells. LNCaP cells were treated with either G47Δ (MOI 1), docetaxel (10 nM) or their combination and at either 24 or 36 h, the percentages of 4N and MPM-2-containing populations were determined by two-color PI and anti-MPM-2 antibody staining. Experiments represent the average±s.e.m. of three independent experiments (f). The 4N-gated populations were analyzed for MPM-2 staining at 24 and 36 h as a function of treatment groups. Note, by 36 h the majority of the 4N cells lack MPM-2 labeling due to G47Δ infection.