Figure 1.
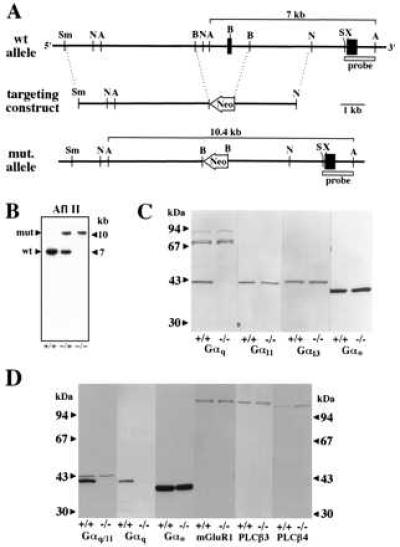
Targeted disruption of the murine Gαq gene. (A) Part of the wild-type Gαq locus containing the two last exons (wt allele), the targeting construct, and the targeted locus (mut. allele) are shown. Neo, neomycin resistance gene. The sizes of the AflII fragments predicted to hybridize to the indicated diagnostic probe are shown. Restriction endonucleases: A, AflII; B, BglII; N, NdeI; S, SacI; Sm, SmaI; and X, XhoI. (B) Southern blot analysis of AflII-digested genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+), hemizygous (−/+), and homozygous mutant mice (−/−) with the diagnostic probe indicated in A. (C) Western blot analysis of whole brain cholate extracts from wild-type (+/+) and homozygous Gαq mutant mice (−/−) with antibodies recognizing the α-subunits of Gq (Gαq), G11 (Gα11), G13 (Gα13), and Go (Gαo). (D) Western blot analysis of cerebellar membrane fractions from wild-type (+/+) and homozygous Gαq mutant animals (−/−) with antibodies recognizing the α-subunits of Gq and G11 (Gαq/Gα11), Go (Gαo), type 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1), phospholipase C-β3 (PLC-β3), and phospholipase C-β4 (PLC-β4).
