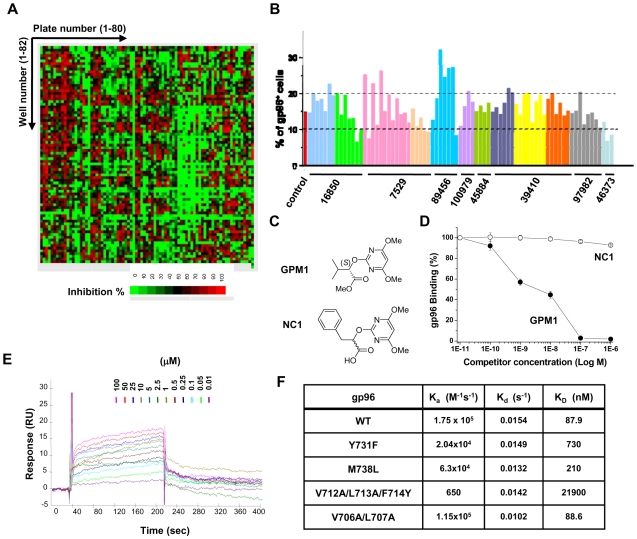
Figure 1. Identification of gp96-binding compound that suppresses plasma membrane levels of gp96.
(A) Heat map of primary screening data. Inhibitory effects of 6,482 chemicals on the interaction of gp96 and AIMP1 were monitored by modified ELISA method as described. Taking the value of DMSO as 0%, the inhibition of each chemical was indicated as relative percentage and the degree of the inhibition was represented by a heat map in a 10% scale from 0 (green) to 100% (red). (B) Effect of the derivatives of the primary hits on surface expression of gp96. RAW264.7 cells were treated with 77 compounds (10µM, 24h) and the effects on surface expression of gp96 were analyzed by flow cytometry. We took 5% changes compared to the control group (15% of the gp96+ cells) as cut-off values. Out of 77 compounds, 8 compounds showed suppressive effect on surface expression of gp96 below 10% whereas 12 compounds showed increased gp96+ cells more than 20%. The numbers indicate the primary hits (see table S1) and the effects of their derivatives are shown as bar graphs. The compounds in the same plate are displayed as one color. (C) Chemical structure of GPM1 and negative control (NC1) used in this study. (D) The dose-dependent effect of GPM1 or NC1 on the AIMP1-gp96 interaction using ELISA method as described. The indicated concentrations of the two compounds and biotin-conjugated murine gp96 were added to AIMP1 coated on the surface of microtiter wells, and gp96 bound to AIMP1 was detected with strepavidin-conjugated peroxidase. (E) The binding of GPM1 to gp96 was examined by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). GPM1 at the indicated concentrations was injected to immobilized gp96 and the binding was measured using Biacore 3000. The response data were processed using data from a reference surface and buffer injections. Each concentration was tested in triplicate. (F) Association rate constant (Ka), dissociation rate constant (Kd), and equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) were determined for the interactions of GPM1 with various mutants of gp96 by the SPR experiments as described in Methods.