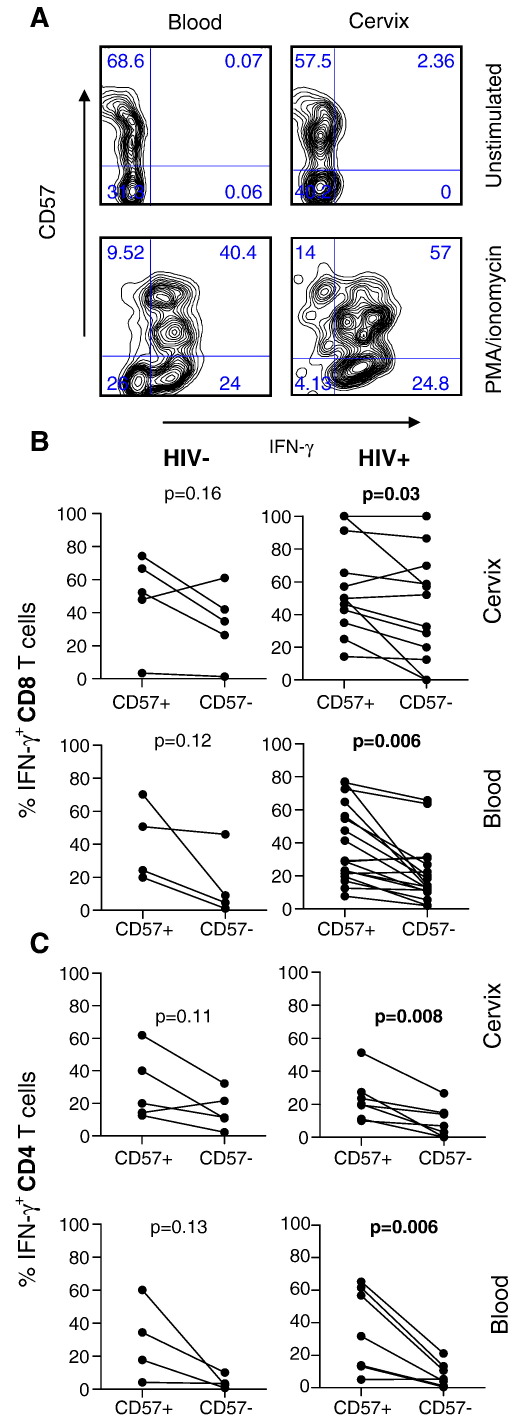
Figure 3.
Comparison of ex vivo IFN-γ production by CD57+ and CD57− T cells derived from the blood and genital mucosa of HIV− and HIV+ women in response to polyclonal stimulation (PMA/ionomycin). (A) Representative plots showing the frequency of IFN-γ production by CD57+ or CD57− CD8+ T cells in the blood (left panels) and cervix (right panels) following PMA/ionomycin stimulation. (B) Net percentages of IFN-γ producing CD57+CD8+ and CD57−CD8+ T cells (percentage of stimulated IFN-γ producing cells minus the percentage of background percentage of unstimulated cells producing IFN-γ) after ex vivo stimulation with PMA/ionomycin were compared in cervical mucosa (upper panel) and blood (lower panel) in HIV− (left panel) and HIV+ (right panel) women. (C) Net percentages of IFN-γ producing CD57+CD4+ and CD57−CD4+ T cells in cervical mucosa (upper panel) and blood (lower panel in uninfected (left panel) in HIV− and HIV+ (right panel) women. Each dot represents an individual's net percentage of CD57+CD8+ or CD57−CD8+ T cells producing IFN-γ at the cervix and in blood. p-values ≤ 0.05 were considered significant. Paired Student's t-test was used to compare IFN-γ frequencies by CD57+ versus CD57− T cells per individual.