Abstract
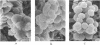
Interactions between clarithromycin and biofilms formed by Staphylococcus epidermidis were investigated by using a clarithromycin-resistant strain. Treatment of the colonization with a relatively low concentration of clarithromycin resulted in the eradication of slime-like structure and a decrease in the quantity of hexose. Another result was increased penetration of antibiotics through the biofilm of S. epidermidis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Costerton J. W. Enhanced activity of combination of tobramycin and piperacillin for eradication of sessile biofilm cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Lucet J. C., Rohner P., Herrmann M., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from infected foreign body in vivo to killing by antimicrobials. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1369–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dall L., Barnes W. G., Lane J. W., Mills J. Enzymatic modification of glycocalyx in the treatment of experimental endocarditis due to viridans streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):736–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson G. M., Bisno A. L. Infections associated with indwelling devices: concepts of pathogenesis; infections associated with intravascular devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):597–601. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Allison D. G., Brown M. R., Gilbert P. Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli biofilms towards ciprofloxacin: effect of specific growth rate. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Feb;27(2):177–184. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber B. F., Kaplan M. H., Clogston A. G. Staphylococcus epidermidis extracted slime inhibits the antimicrobial action of glycopeptide antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):37–40. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. D., Peters G., Verstegen M., Regelmann W. E. Effect of extracellular slime substance from Staphylococcus epidermidis on the human cellular immune response. Lancet. 1984 Feb 18;1(8373):365–367. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gristina A. G., Hobgood C. D., Webb L. X., Myrvik Q. N. Adhesive colonization of biomaterials and antibiotic resistance. Biomaterials. 1987 Nov;8(6):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(87)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. M., Lee D. A., Regelmann W. E., Gray E. D., Peters G., Quie P. G. Interference with granulocyte function by Staphylococcus epidermidis slime. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam J., Chan R., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Production of mucoid microcolonies by Pseudomonas aeruginosa within infected lungs in cystic fibrosis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):546–556. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.546-556.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Costerton J. W. Mode of growth of bacterial pathogens in chronic polymicrobial human osteomyelitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):924–933. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.924-933.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberry-Carson K. J., Tober-Meyer B., Smith J. K., Lambe D. W., Jr, Costerton J. W. Bacterial adherence and glycocalyx formation in osteomyelitis experimentally induced with Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):825–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.825-833.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser B. L., Taylor D., Dix B. A., Cleeland R. Method of evaluating effects of antibiotics on bacterial biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1502–1506. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROE J. H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STICKLAND L. H. The determination of small quantities of bacteria by means of the biuret reaction. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):698–703. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda H., Oogaki N., Kikuchi N., Kobayashi H., Akashi T. [A study to clarify the mechanism of the usefulness of the macrolides--the influence of clarithromycin to biofilm with P. aeruginosa]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1992 Oct;66(10):1454–1461. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.66.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Zulian G., Huggler E., Waldvogel F. A. Attachment of Staphylococcus aureus to polymethylmethacrylate increases its resistance to phagocytosis in foreign body infection. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):472–477. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.472-477.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren J. W., Muncie H. L., Jr, Bergquist E. J., Hoopes J. M. Sequelae and management of urinary infection in the patient requiring chronic catheterization. J Urol. 1981 Jan;125(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)54874-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Wiestner A., Frei R., Zimmerli W. Killing of nongrowing and adherent Escherichia coli determines drug efficacy in device-related infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):741–746. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Ajiki Y., Koga T., Kawada H., Yokota T. Interaction between biofilms formed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and clarithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Sep;37(9):1749–1755. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.9.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]