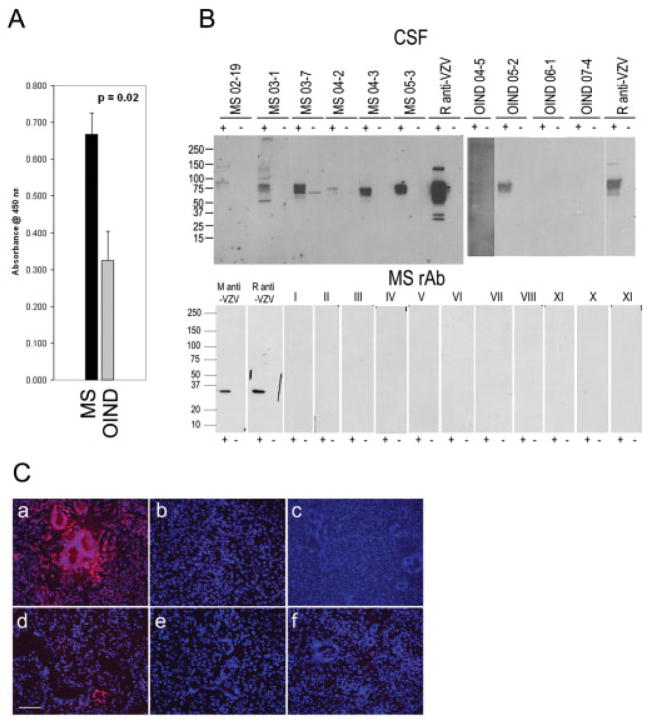
Fig 2.
Analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and recombinant antibodies (rAbs) prepared from clonally expanded plasma cells in multiple sclerosis (MS) cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for varicella zoster virus (VZV) reactivity. (A) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis of human CSF binding to VZV. CSF samples from patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and other inflammatory neurological diseases (OIND) were diluted to IgG concentrations of 10μg/ml and reacted with VZV-infected cell lysates. The eight OIND were VZV vasculopathy, cryptococcal meningitis, chronic meningitis, subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) (2), paraneoplastic syndrome, neurosyphilis, and meningoencephalitis. Panel shows the average reactivity (± SEM) of MS CSF compared to average reactivity of OIND. (B) Immunoblotting of MS IgG with VZV. Lysates of VZV-infected (+) or uninfected (−) MeWo cells were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitro-cellulose membranes, and reacted with 5μg/ml IgG from MS CSF, rabbit anti-VZV, or OIND IgG. Positive control anti-VZV monoclonal antibody (M anti-VZV), polyclonal rabbit anti-VZV IgG antibody (R anti-VZV), and recombinant antibodies (rAbs) prepared from clonally expanded plasma cells in MS CSF (5μg/ml) were used to immunoblot VZV-infected and uninfected cell lysates. All rAbs were negative (lanes I-XI). Molecular size is given in kilodaltons. (C) Immunostaining. VZV-infected (a) and un-infected (b) MeWo cells were stained with rabbit anti-VZV IgG. The same MS CSF rAbs used in immunoblotting were pooled into nine groups of three to five rAbs (5μg/ml of each rAb) and used to stain VZV-infected MeWo cells. Representative staining is indicated in panels c through f. Note overall lack of reactivity of rAbs with VZV. Bar = 100μm.