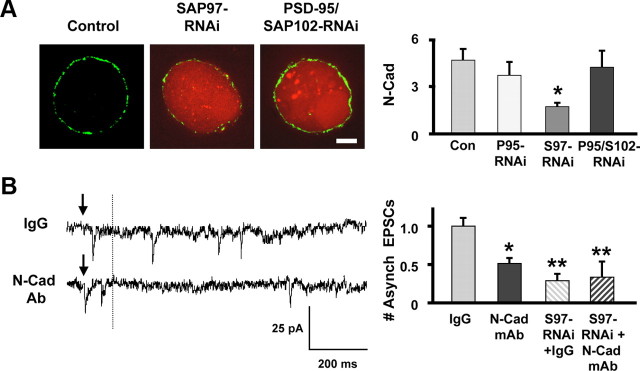
Figure 5.
SAP97 knockdown impairs N-cadherin expression, a transmembrane protein important for asynchronous release. A, Left, CG neurons expressing RNAi constructs targeting PSD-95 family members (red) were immunostained for N-cadherin (green). Right, N-Cadherin (N-Cad) levels were reduced by SAP97 (S97-RNAi) but not by PSD-95 (P95-RNAi) or PSD-95/SAP102 (P95/S102-RNAi) knockdown (*p ≤ 0.05 by ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test; 5–17 cultures/condition). Scale bar, 5 μm. B, Disruption of N-cadherin interactions with a function blocking mAb (N-Cad mAb) selectively impaired asynchronous release. Left, Traces showing asynchronous release (as in Fig. 4B) with cells treated with IgG (control) or N-Cad mAb. Right, Quantification showing that the N-Cad mAb effect was equivalent to but not additive with the SAP-97-RNAi effect on asynchronous release (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01 by ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test; 6 cultures/condition).