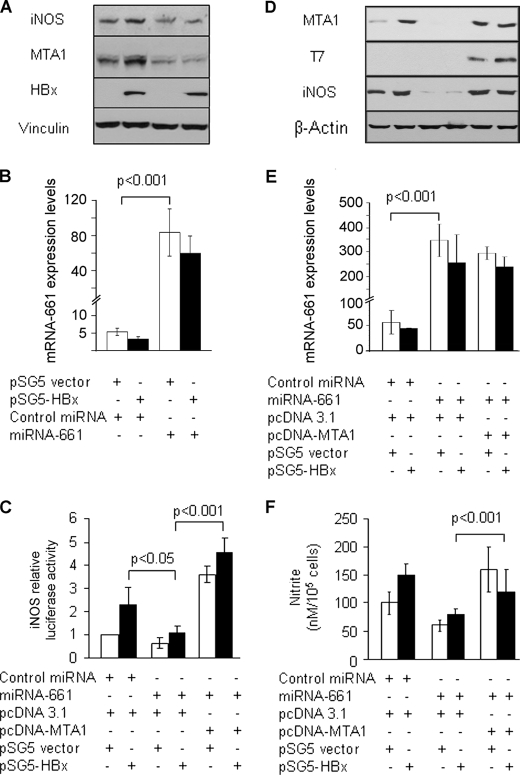
FIGURE 2.
miR-661 plays an instrumental role in HBx regulating iNOS. Effects of miR-661 on HepG2 cells expressing HBx. HepG2 cells were transfected with 100 nmol of either miR-661 or negative control mimic (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO) using Oligofectamine (Invitrogen). After 24 h, transfected HepG2 cells were again subjected to co-transfection with either control vector or HBx (250 ng/reaction in a 6-well plate) and iNOS promoter reporter construct. A and B, cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis for iNOS, HBx, and MTA1 expression. Vinculin was used as a loading control. Transfection efficiency of miR-661 in HepG2 cells was evaluated by quantitative real time PCR. U6 RNA was used as an internal control for miR-661 quantification. C, MTA1 ectopic expression rescued miR-661 effects. iNOS promoter luciferase assay was performed 48 h after HBx transfection. MicroRNA-transfected HepG2 cells were subsequently co-transfected with HBx and pcDNA-MTA1-T7-tagged or control expression vector (500 ng/reaction in a 6-well plate) (n = 3). Results are presented in -fold change compared with control, mean ± S.E., n = 3. D and E, cells were subjected to Western blot analysis for iNOS and MTA1 expression. T7 tag was analyzed for transfection efficiency. β-Actin was used as an internal control. E, transfection efficiency of miR-661 in HepG2 cells being transfected with miRNA-661, HBx, and MTA1 expression vector was evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR. U6 RNA was used as an internal control for miR-661 quantification. F, conditioned medium at the time of harvesting was collected and assayed for nitrite levels as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The levels of nitrite accumulation/105 cells are presented as mean ± S.E. All experiments were repeated at least three times.