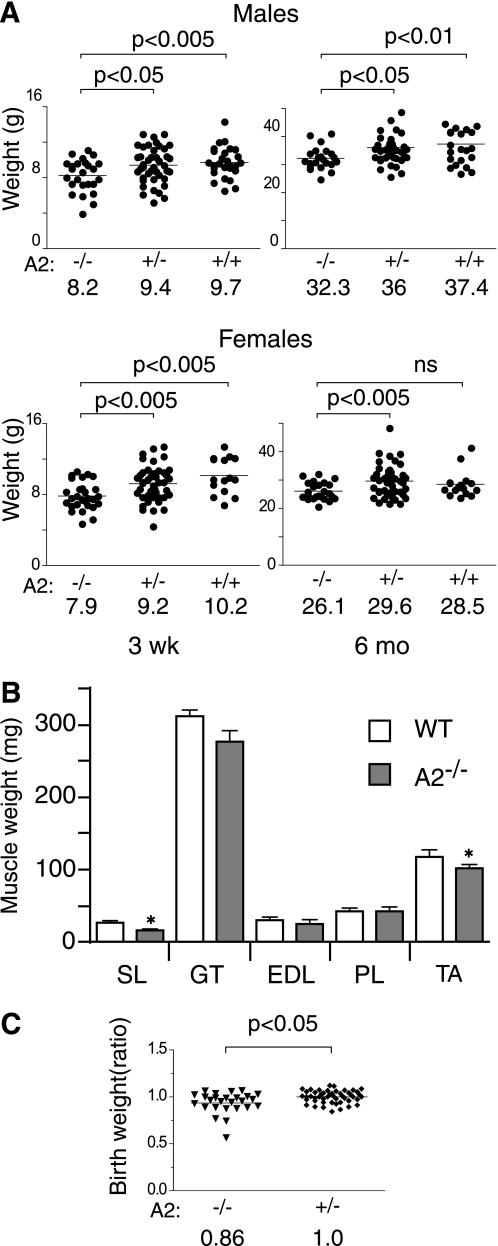
FIGURE 4.
APOBEC2-deficient mice weigh less than control siblings. A, the body weights of APOBEC2 (A2)-deficient (−/−), heterozygous (+/−), and wild-type (+/+) mice from heterozygous breedings were determined at the time of weaning (21 days after birth) and at 6 months. The mean weights for the different groups are indicated. Data were analyzed using Student's t test, with the significance for each comparison shown. ns, not significant. B, the weights of individual muscles from groups of five male 15-week-old wild-type (WT) and five male 15-week-old APOBEC2-deficient mice are shown. SL, soleus muscle; GT, gastrocnemius muscle; PT, plantaris muscle; TA, tibialis anterior muscle. Error bars are means ± S.E., with asterisks denoting differences significant at p < 0.05 (Student's t test). C, the body weights of newborn mice born to breedings of an APOBEC2-deficient father and a heterozygous mother are presented, with the individual weights given as a ratio of the absolute weight of an individual animal to that of the mean of APOBEC2+/− heterozygotes within the same litter.