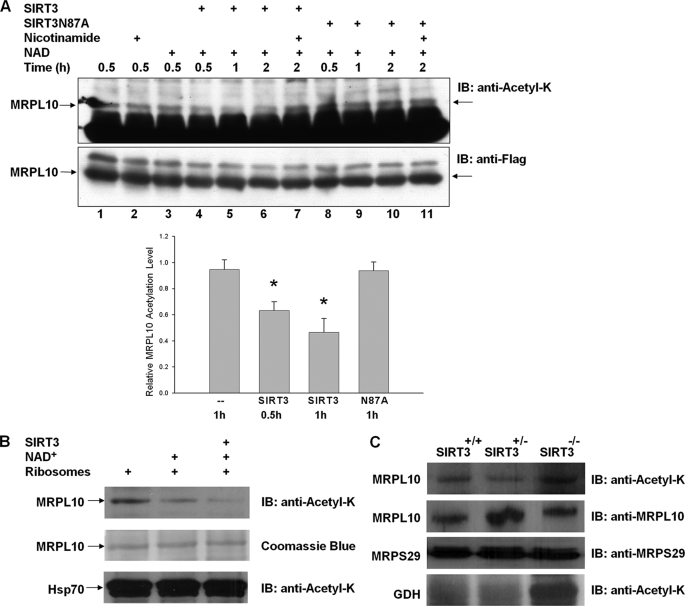
FIGURE 6.
Deacetylation of MRPL10 by NAD+-dependent deacetylase, SIRT3. A, MRPL10 protein was produced by transfecting FLAG-tagged MRPL10 into HEK293 cells and then immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG-agarose beads. Purified MRPL10 was then incubated with or without recombinant SIRT3 or SIRT3 mutant, SIRT3N87A, together with 10 mm nicotinamide or 5 mm NAD+, as indicated. The acetylation of MRPL10 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-N-acetyl lysine. *, p < 0.005. B, in vitro deacetylation reactions of about 0.1 A260 units of 55 S bovine mitochondrial ribosomes were performed in the presence of 3 mm NAD+ and 0.2 μg of recombinant SIRT3 as labeled and detected by immunoblotting (IB) analysis probed with anti-N-acetyl lysine antibody. The arrows indicate the specific deacetylation of MRPL10 but not the acetylated Hsp70 sedimented with ribosomes by endogenous and recombinant SIRT3 in the presence of 3 mm NAD+. C, mitochondrial ribosomes were prepared as described under “Experimental Procedures” from Sirt3−/−, Sirt3+/−, and Sirt3+/+ mouse liver, and the acetylation of ribosomal protein MRPL10 was detected by immunoblot analysis probed with anti-N-acetyl lysine antibody. As a control for acetylation of glutamate dehydrogenase in the absence of SIRT3 and equal loading, immunoblots were developed with anti-N-acetyl lysine and mouse MRPL10 and MRPS29 antibodies.