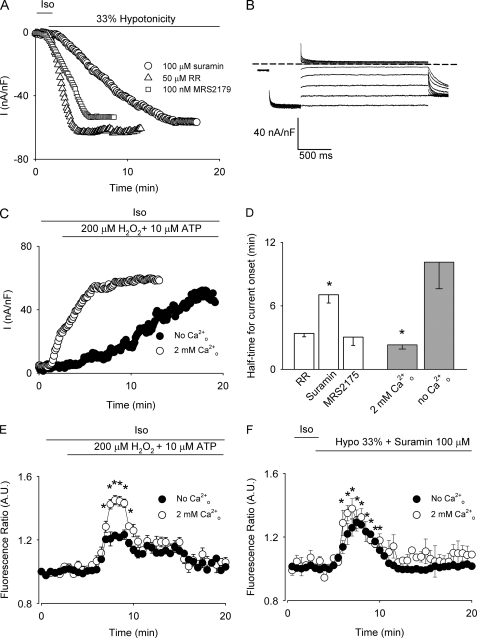
FIGURE 3.
Effect of purinergic receptor activity on VSOR Cl− currents. A, representative experiment of the time course of VSOR Cl− currents in cells exposed to 33% hypotonicity and 50 μm ruthenium red (▵), 100 μm suramin (○), or 100 nm MRS2175 (□). Currents were recorded at −80 mV every 7 s, and normalized to cell capacitance. B, representative steady-state nystatin-perforated whole-cell current traces obtained using the same protocol as in Fig. 1, A and B of a cell exposed to 33% hypotonicity and 100 μm suramin. C, representative time course of VSOR Cl− currents in cells exposed to 200 μm H2O2 and 10 μm ATP in the presence (○) or absence (●) of external Ca2+. The experimental protocol is as in Fig. 1C. D, summary of the data for half-time for current onset obtained from n = 5–6 independent experiments for 33% hypotonic solution (empty bars) or 200 μm H2O2 plus 10 μm ATP (light gray bars)-stimulated cells. E, time course of Cai2+ signal (averaged fluorescence ratio ± S.E.). Cells were exposed to 200 μm H2O2 and 10 μm ATP during the time depicted by the bar in the presence (○, control) or absence of external Ca2+ (●). n = 4 independent experiments. F, time course of Cai2+ signal (averaged fluorescence ratio ± S.E.). Cells were exposed to 33% hypotonicity and 100 μm suramin during the time depicted by the bar in the presence (○, control) or absence of external Ca2+ (●). n = 5 independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 compared with control conditions.