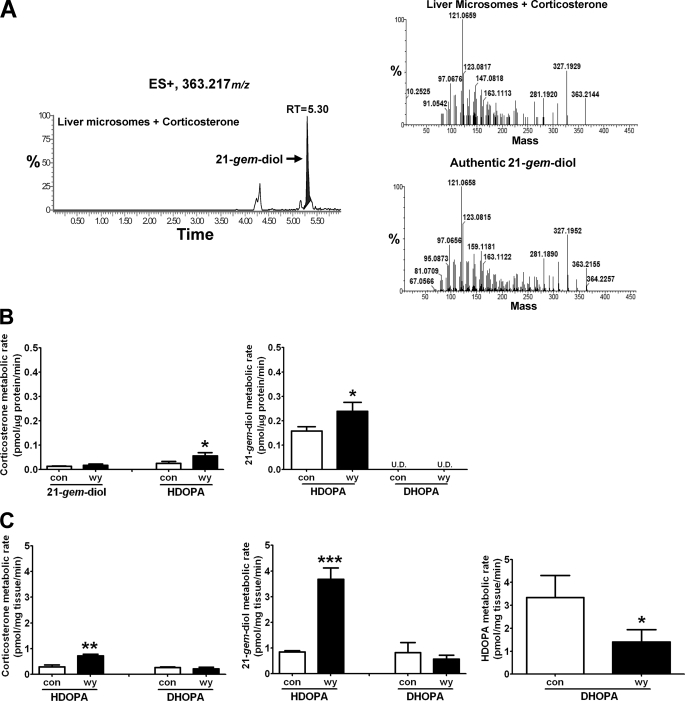
FIGURE 5.
Identification of 21-gem-diol as the intermediate in the metabolic pathway forming HDOPA and 20α-DHOPA. Wild-type mice were fed control or WY diet for 1 week before collecting livers. Liver microsomes and homogenates were prepared and analyzed by UPLC-TOFMS. In metabolic studies, 50 μm of corticosterone, 21-gem-diol, HDOPA, and 20α-DHOPA were incubated separately with liver microsomes or homogenates for 30 min. The mass spectra from incubation samples including both tissue and substrate were compared with the incubation solution with only the substrate using MetaboLynx to find potential metabolites. The concentration of each metabolite was obtained from QuanLynx using debrisoquine as internal standard. A, chromatogram of a corticosterone metabolite produced from liver microsomes (left panel), whose MS/MS spectrum (right top panel) and retention time (m/z = 363.217+ at 5.30 min) matched that of authentic 21-gem-diol standard (right bottom panel). B, the activities of liver microsomes in the metabolism of corticosterone (left) and 21-gem-diol (right panel) (n = 3). C, the activities of liver homogenates in the metabolism of corticosterone (left panel), 21-gem-diol (middle panel), and HDOPA (right panel) (n = 3). Each data bar in this figure represents the mean ± S.D. DHOPA, 20α-DHOPA; U.D., undetectable. The group differences are shown with significance values of p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), and p < 0.001 (***).