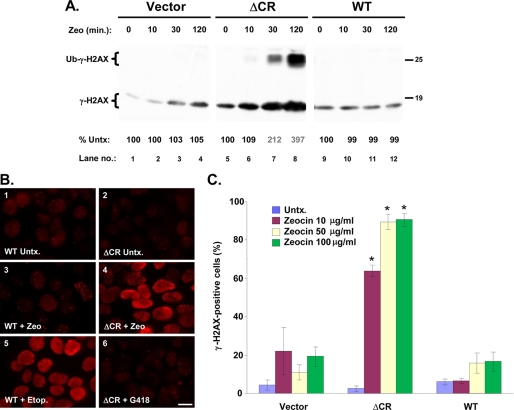
FIGURE 7.
Zeocin rapidly induces DNA damage in cells expressing ΔCR PrP. A, HEK cells stably transfected with empty vector or with vector encoding ΔCR or WT PrP were incubated with Zeocin (500 μg/ml) for the indicated times, after which cells were lysed, and γ-H2AX was detected by Western blotting. When large amounts of γ-H2AX are present, a monoubiquitinated form becomes visible (Ub-γ-H2AX; lanes 7 and 8). The numbers below each lane indicate the amount of γ-H2AX, expressed as a percentage of that in untreated control cells. B, HEK cells expressing WT or ΔCR PrP were untreated (Untx.) (panels 1 and 2) or were incubated for 60 min with Zeocin (100 μg/ml) (panels 3 and 4), etoposide (50 μm) (panel 5), or G418 (1,000 μg/ml) (panel 6). Cells were then fixed and stained with an antibody to γ-H2AX antibody and viewed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar in panel 6, 5 μm. C, HEK cells expressing vector, WT PrP, or ΔCR PrP were left untreated (untx) or were incubated for 60 min with the indicated concentrations of Zeocin. Cells were then stained for γ-H2AX and analyzed by semiautomated microscopy (see “Experimental Procedures”). The bars show the mean percentage ± S.E. of γ-H2AX-positive cells (nine separate fields, 1,000 total cells/well) from two independent experiments. *, values that are significantly different from corresponding values for vector and WT (p < 10−8).