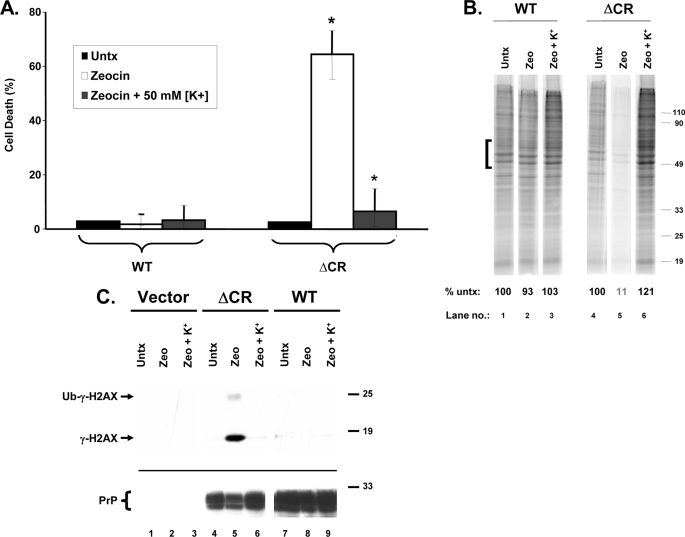
FIGURE 9.
ΔCR PrP-induced drug toxicity is blocked by elevated extracellular [K+]. A, HEK cells expressing WT or ΔCR PrP were treated for 48 h with Zeocin (500 μg/ml), either in normal extracellular [K+] (5 mm) or in elevated extracellular [K+] (50 mm). Cell viability was then assayed by MTT reduction. Cell death (1 − A570) is plotted as a percentage of the value for non-drug-treated cells (Untx) in 5 mm [K+]. The bars represent means ± S.E. from three independent experiments. The values indicated by the asterisks are significantly different from each other (p < 0.02). B, HEK cells expressing WT or ΔCR PrP were untreated (lanes 1 and 4) or were incubated for 20 h with Zeocin (1,000 μg/ml) (lanes 2, 3, 5, and 6), either in 5 mm [K+] (lanes 1, 2, 4, and 5) or in 50 mm [K+] (lanes 3 and 6). Cells were then labeled with [35S]methionine and analyzed by SDS-PAGE as described in the legend to Fig. 6. The numbers below each lane indicate the amount of radioactivity incorporated in the region indicated by the bracket, expressed as a percentage of that in untreated control cells (lanes 1 and 4). C, HEK cells expressing vector, ΔCR PrP, or WT PrP were incubated for 24 h with Zeocin (100 μg/ml), either in 5 mm [K+] (lanes 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, and 8) or in 50 mm [K+] (lanes 3, 6, and 9). Cells were lysed and analyzed for γ-H2AX by Western blotting (top). PrP levels were verified by reprobing the blot with 6D11 antibody (bottom).