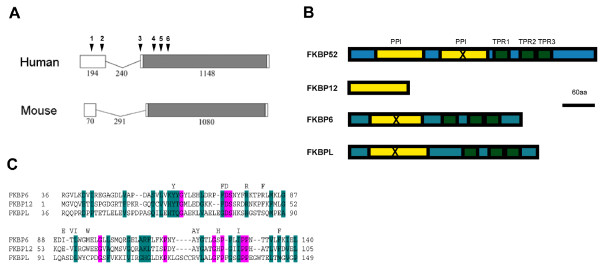
Figure 1.
FKBPL structure and conservation. A. Structure of the human and mouse genes. The gene consists of two exons, joined by a short intron. The open reading frame is in grey, lengths in base pairs are indicated. The positions of the gene alterations seen in patients and listed in Table 1 are indicated above the human sequence. B. Protein structure. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPI) domains are shown in yellow, tetratricopeptide repeats (TPR) in green. FKBP12 has a PPI domain but contains no TPR. FKBP52 and FKBP51 contain a duplication of the PPI domain, but the C-terminal copy is inactive (X). FKBP6 and FKBPL have N-terminal regions with some homology to the PPI.C. Alignment of the PPI domains from FKBP6, FKBP12 and FKBPL by CLUSTALW: residues conserved in PPI with good enzymatic activity are indicated above the alignment but can be seen to be poorly conserved in FKBPL.